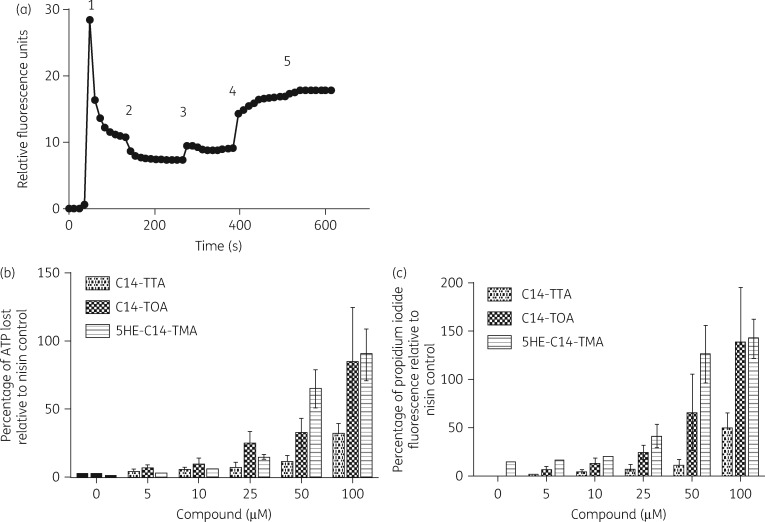
Figure 2.
Perturbation of staphylococcal cytoplasmic membrane structure and function by 5HE-C14-TMA, C14-TTA and C14-TOA. (a) Depolarization of transmembrane potential by 5HE-C14-TMA. (1) Cationic fluorescent dye DiSC3(5) was added to cells followed (2) by glucose (10 mM), (3) nigericin (5 μM) to abolish the pH gradient and (4) 5HE-C14-TMA (30 μM). Complete depolarization of the membrane potential was achieved by the addition of 5 μM valinomycin (5). Experiments were carried out on three independent occasions with representative data presented. (b) Cytoplasmic ATP release relative to the positive control (nisin, 0.6 μM) of S. aureus cells treated with (from left to right) 0, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 μM 5HE-C14-TMA, C14-TTA or C14-TOA. (c) Membrane permeability. The percentage of propidium iodide uptake relative to the positive control (nisin, 0.6 μM) of S. aureus cells treated with (from left to right) 0, 5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 μM 5HE-C14-TMA, C14-TTA or C14-TOA. Data plotted are the mean values of three independent experiments; error bars represent standard deviations.