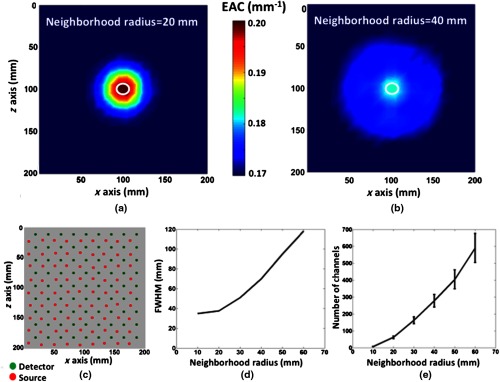
Fig. 5.
(a and b) Topographic images of EAC obtained with simulated FEM data on a cubic medium (, 15 mm minimum interoptode distance grid, , , with a cylindrical 10-mm-diameter absorption inhomogeneity, , up to 40 mm depth). (a) Topographic image obtained with a neighborhood radius of 20 mm. The white circle indicates the actual position and shape of the inhomogeneity. (b) Topographic image obtained with a neighborhood radius of 40 mm. The white circle indicates the actual position and shape of the inhomogeneity. (c) Optode array used for the simulations (15 mm minimum interoptode distance grid). (d) FWHM of the image reconstruction procedure as a function of the neighborhood radius. (e) Average number of channels, and related standard deviation, involved in the computation of each channel’s EAC as a function of the neighborhood radius.