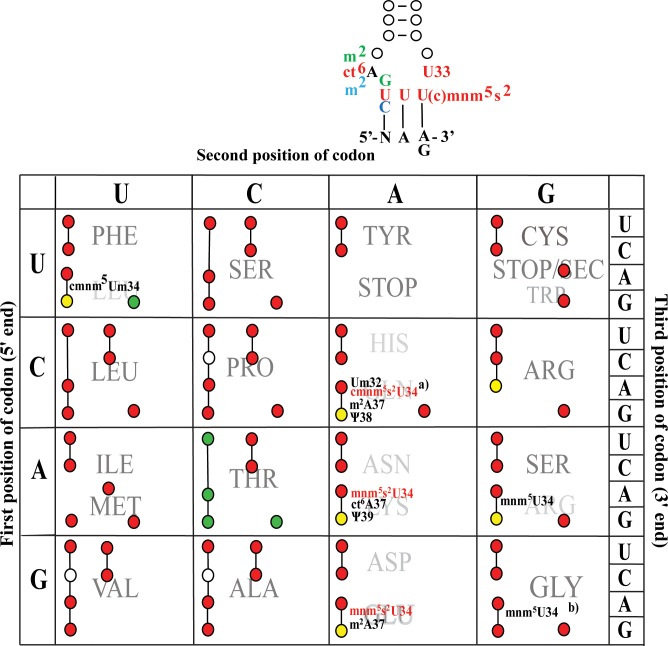
Fig 2. Codon table and the anticodon loop of tRNAs specific for Gln, Lys, and Glu which contain cmnm5s2U (Gln) or mnm5s2U (Lys and Glu) as wobble nucleoside in bacterial tRNAs.
Above the third column (second codon base A) the anticodon stem and loop of the tRNAs containing the (c)mnm5s2U in position 34 is shown (denoted in red cmnm5s2). Position 36 of the anticodon is color coded with Green G36 being position 36 for , red U36 for , and blue C36 for . Similar color code is denoted for the modified nucleosides present in position 37 in the corresponding tRNAs. N denotes G, A or C, respectively, for first nucleoside in the relevant codons read by these tRNAs. Note that these tRNAs are rich in U, which is a poor stacker [24] making the anticodon very flexible especially if the modifications is absent and this is especially true of . In the codon table the letters outside the box, to the left, above, and to the right indicate the first, second, and third position of the codon. Circles connected by a line, or a single circle, represent one tRNA species. A filled circle indicates the capacity of that tRNA to base pair with the indicated codon, either by Watson-Crick or by wobble according to the revised wobble hypothesis [1]. Red and yellow circles indicate tRNAs that are sequenced at the RNA level while green circles represent tRNAs for which only a partial tRNA sequence is available. A red or green circle indicates efficient base pairing while a yellow circle indicates a restricted wobble. An open (white) circle is a base pairing that is not according to the revised wobble hypothesis. However, data in vivo from mutants where only this tRNA is left to decode all codons in the codon box, suggest that the tRNA in fact is able to read that codon [9, 25]. Data are compiled from Sprinzl data base (http://trnadb.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de/ and Modomics data base (http://modomics.genesilico.pl/). Mutations in mnmE or mnmG genes result in no formation of the (c)mnm5- group not only of the (c)mnm5s2U present in tRNAs specific for Gln, Lys and Glu but also cmnm5Um in and mnm5U34 in tRNAs specific for Arg and Gly. Mutations in mnmA results in no thiolation of cmnm5s2U34. a) The modifications in position 34 of from S. enterica are cmnm5s2U (80%) and mnm5s2U (20%) [10] and similar in E. coli [11] b) The majority of this tRNAGly contains mnm5U34 but there is also a small amount of cmnm5U34 [1].