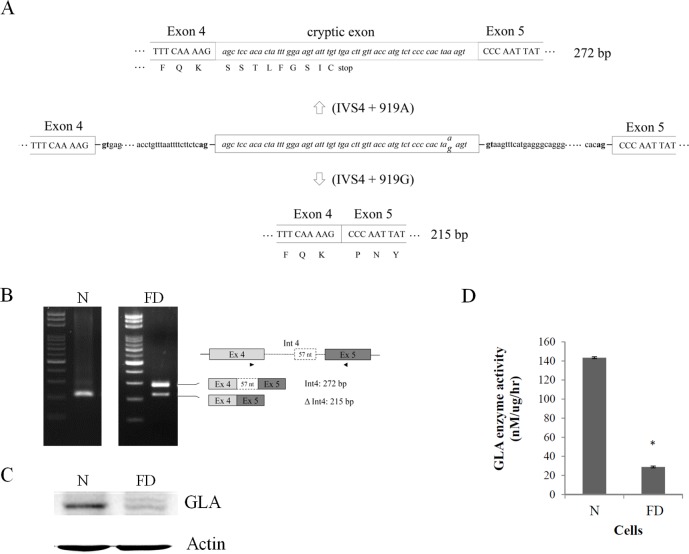
Fig 1. Alternative splicing of GLA (IVS4 + 919G>A).
(A) Schematic representation of GLA. Uppercase letters indicate the exonic sequences, whereas lowercase letters indicate the intronic sequences. The encoded amino acids are depicted in single-letter code. The invariant AG and GT dinucleotides (the 3’ and 5’ splice sites) are shown in boldface type. The alternatively spliced 57 nucleotide sequence is enclosed in the box with italics letters. (B) Messenger RNA was extracted and detected by RT-PCR for alternative splicing of GLA (IVS4 + 919G>A). The splicing variants and their expected PCR products using the primers indicated by arrowheads are illustrated on the right column. (C) Aliquots containing 20 μg of whole cell lysates was subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using an anti-GLA antibody. Actin was shown as internal standard. (D) The result of enzyme activity assay from lymphoid cell lines of health person and FD patient. Data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. Asterisk represents significant difference (p-value < 0.05). N, normal cells; FD, Fabry disease cells.