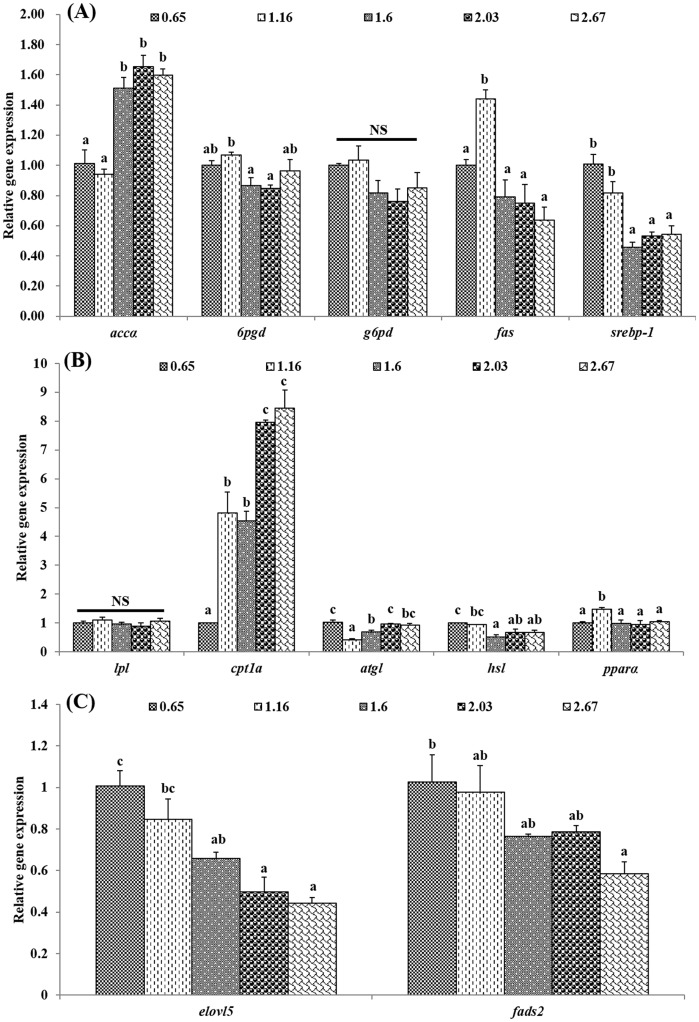
Fig 1. Effects of dietary DHA/EPA ratio on relative mRNA expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism pathways including anabolism (A), catabolism (B) and LC-PUFA biosynthesis (C) in the liver of juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii).
The control group (0.65 DHA/EPA) was used as the reference group, and the mRNA expression levels of target genes were normalized relative to the expression of β-actin. Values are means (n = 3), with standard errors represented by vertical bars. Mean values for the same gene with different letters were significantly different (P < 0.05). accα, acetyl-CoA carboxylase alfa; 6pgd, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; g6pd, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; fas, fatty acid synthase, srebp-1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1; lpl, lipoprotein lipase; cpt1a, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; atgl, adipose triglyceride lipase; hsl, hormone-sensitive lipase; pparα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; fads2, fatty acyl desaturase 2 and elovl5, elongase of very long-chain fatty acids 5. NS, not significant.