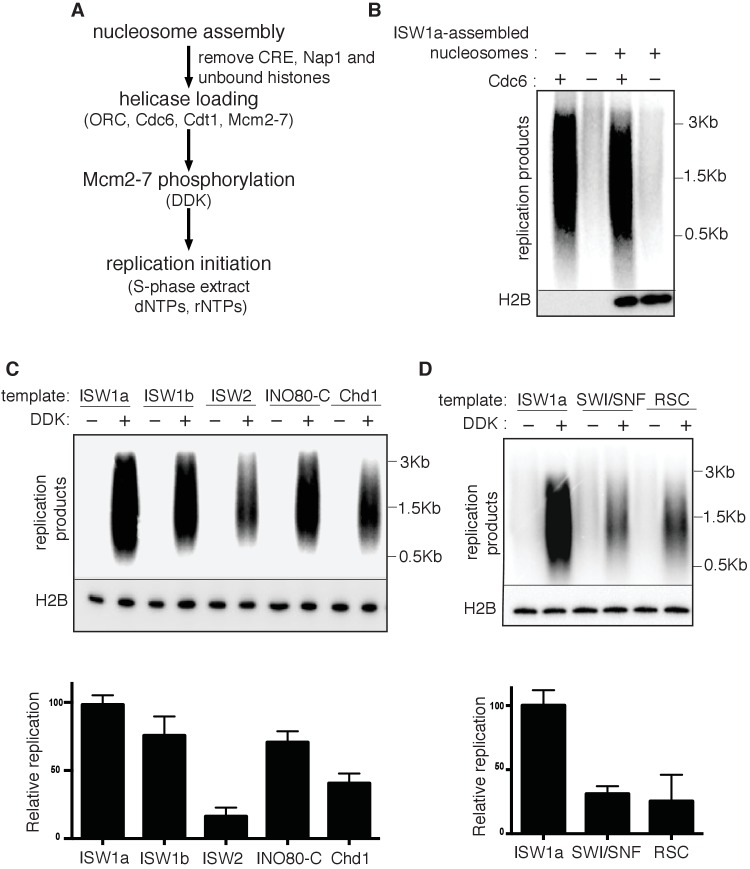
Figure 3. Replication initiation on nucleosome templates.
(A) Outline of nucleosomal DNA replication initiation assay using purified proteins and yeast S-phase cell extract. (B) ISW1a templates do not interfere with replication. Naked DNA or ISW1a templates were assayed in the presence or absence of Cdc6. Radiolabeled replication products were analyzed by alkaline agarose electrophoresis and autoradiography (top). Template-associated H2B was detected by immunoblot (lower). (C) Comparison of replication using ISW1a, ISW1b, ISW2, INO80-C and Chd1 templates in the presence and absence of DDK. Products of the extract-based replication assays were analyzed as in (B, top). H2B levels for each template are shown (middle). Quantification of replication products was performed as in Figure 2B. Error bars show the SD (n = 3, lower). (D) Comparison of replication of ISW1a, SWI/SNF and RSC templates in the presence or absence of DDK. Analysis of replication products, template-associated H2B and quantification (n = 3) as in (C).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22512.012
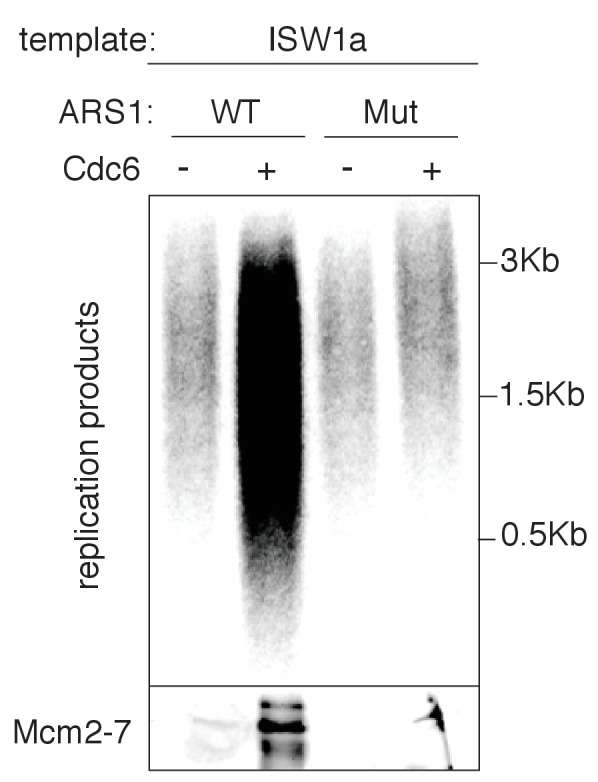
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. In vitro nucleosomal DNA template replication initiation is origin specific.