Figure 5. Anti-tumorigenic effect of Axl-induced LIGHT expression in EL4 T lymphoma-bearing mice. WT mice injected with EL4-Axl cells and mock controls were sacrificed at 21 days (n=8).
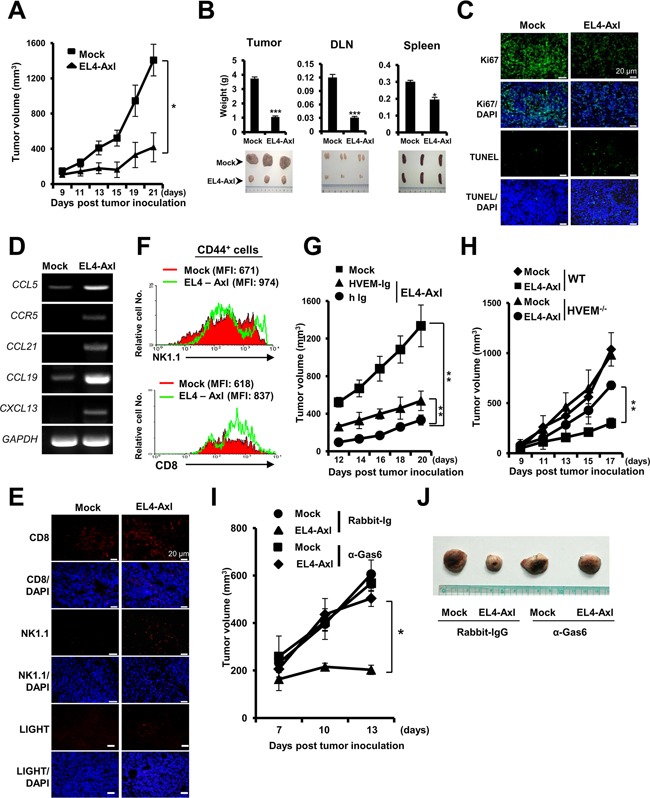
(A and B) Changes in the volume (A), weight (B, left and top) and shape (B, left and bottom) of tumors are shown. The weight and shape of the draining lymph node (DLN) and spleen from the indicated mice are shown. Tumor progression-associated molecules were evaluated as follows: (C and E) Immunohistofluorescence analysis using the indicated antibodies. (D) qRT-PCR using each chemokine-specific primer. (F) In the flow cytometry analysis, the activation status of CTLs and NK cells was determined by mean fluorescence intensity of CD8+ or NK1.1+ cells on gated CD44+ cells. (G and H) Tumor volume of HVEM-Ig-administered EL4-Axl tumor-bearing WT mice and of EL4-Axl tumor-bearing in HVEM−/− mice. (I and J) Tumor volume and size of the Gas6-deficient EL4-Axl-bearing mice (n=4). The data from A, B, D, G and H are shown as the mean ± SEM (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001). Data are representative of five independent experiments.
