Figure 7. P-Akt is essential for the anti-fibrotic effects of IDA in CCl4-treated mice and TGF-β-treated LX2 cells.
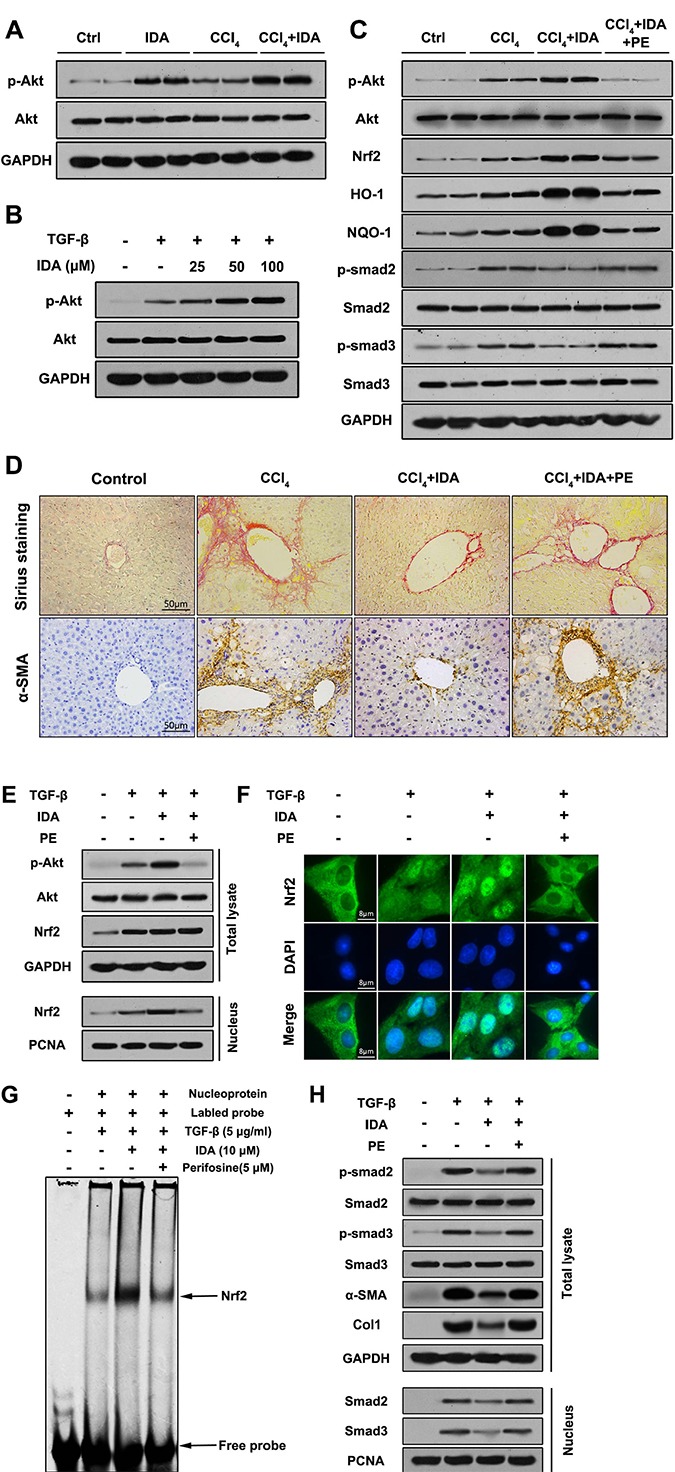
(A) The expressions of p-Akt and Akt in liver tissues were measured by western blotting (Two randomly samples in each group were represented). (B) LX2 cells were pretreated with series doses of IDA (25 μM, 50 μM or 100 μM) for 1 h and then treated with or without TGF-β (5 ng/ml) for another 1 h. The expressions of p-Akt and Akt were measured by western blotting. (C) C57BL/6 mice were injected with CCl4, IDA (20 mg/kg/wk) and (or) Perifosine (60 mg/kg/wk) for 8 weeks. The p-Akt, Akt, Nrf2, HO-1, NQO-1, p-Smad2, Smad2, p- Smad3 and Smad3 in liver tissues were measured by western blotting (Two random selected samples in each group). (D) Representative images of Sirius Red staining and immunohistochemistry of α-SMA in liver. (n = 6 in each group). (E) LX2 cells pretreated with PE (5 μM) and (or) IDA (100 μM) for 1 h and next treated with or without TGF-β for 1 h. The p-Akt, Akt and Nrf2 in total lysate and Nrf2 in nucleus were measured by western blotting. (F) The nuclear translocations of Nrf2 were determined by immunofluorescence assay. (G) The DNA binding activity of Nrf2 were measured by EMSA. (H) The p-Smad2, p-Smad3, Smad2, Smad3, α-SMA and Col1 in total lysates and Smad2 and Smad3 in nucleus were measured by western blotting.
