Figure 1. Association between prostate cancer and vitamin D status.
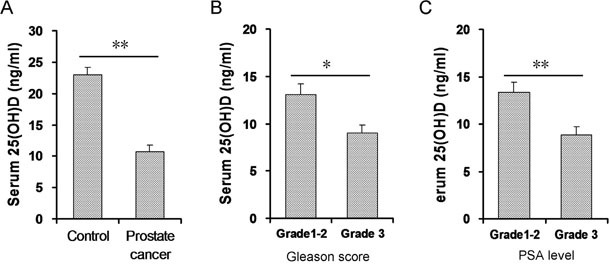
Serum 25-(OH)D was measured by RIA. (A) Serum 25(OH)D level was compared between patients with prostate cancer and controls. (N=60 for patients with prostate cancer; N=120 for controls). (B) Patients with prostate cancer were divided into two groups according to Gleason score: mild and moderate prostate cancer (n=34) and severe prostate cancer (n=26). Serum 25(OH)D level was compared between two groups. (C) Patients with prostate cancer were divided into two groups according to serum PSA level: mild and moderate prostate cancer (n=31) and severe prostate cancer (n=29). Serum 25(OH)D level was compared between two groups. All data were expressed as means ± S.E.M. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.
