Figure 1. S. pneumoniae CSP-mediated QS circuit.
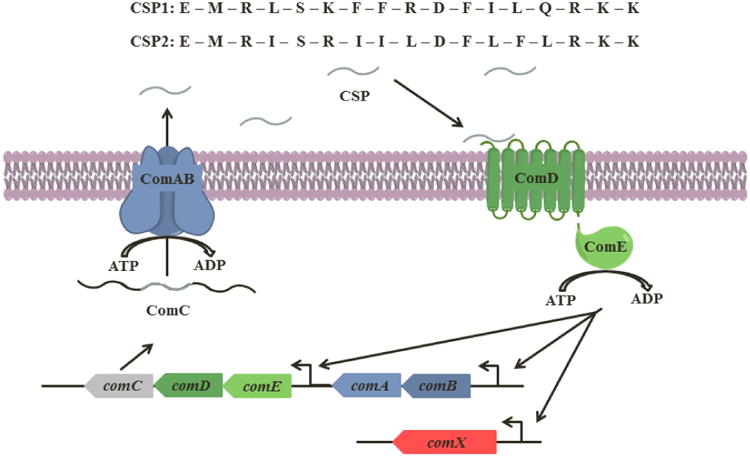
The CSP pro-peptide, ComC, is processed intracellularly and secreted by the ABC transporter (ComAB) as the mature CSP. When the extracellular CSP concentration reaches a threshold concentration, it can effectively bind and activate its cognate receptor, ComD. Activation of ComD leads to phosphorylation of ComE, a response regulator, and results in the autoinduction of the QS circuitry (ComABCDE) and expression of comX, which codes for QS-regulated phenotypes. Thus far, two major specificity groups of S. pneumoniae have been identified, each having a unique signaling peptide (CSP1 and CSP2) and corresponding cognate receptor (ComD1 and ComD2). Both CSPs are 17-amino acid peptide signals (written in one-letter code) and vary mainly in their central region.
