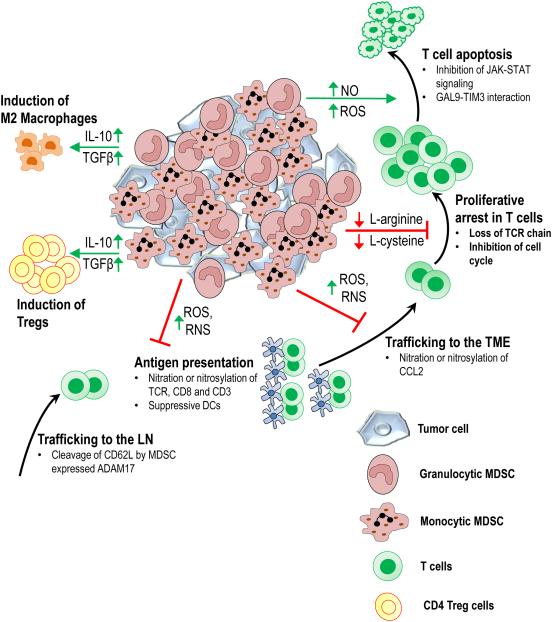
Figure 2. Mechanisms of MDSC-mediated immunosuppression.
MDSCs within and outside the TME can suppress anti-tumor immunity in a variety of ways. Cleavage of CD62L from the surface of T cells by MDSC expressed ADAM17 blocks naïve T cell migration to lymph nodes, where they would be activated by antigen presenting cells. Through production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), MDSCs interfere with T cell activation and recruitment to the TME. By depleting arginine and cysteine from the extracellular environment of the T cells, MDSCs induce proliferative arrest in T cells. Additionally through the release of cytokines such as IL-10 and TGFβ, MDSCs promote induction of Tregs and M2 macrophage polarization.