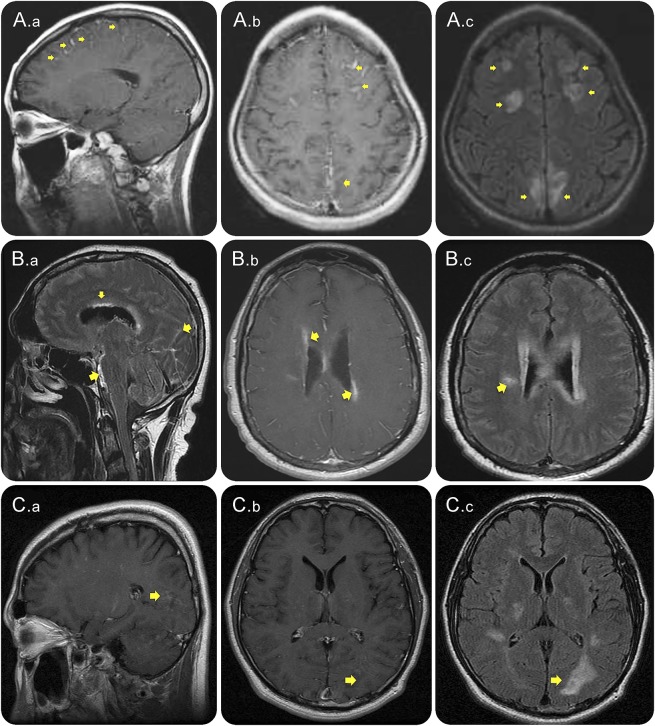
Figure 1. Leptomeningeal enhancement accompanied by intraparenchymal enhancement during attacks in patients with NMOSD.
Contrast-enhanced cerebral T1W (A.a, A.b, B.b, C.a, and C.b), FLAIR sequences (A.c, B.a, B.c, and C.c) and FLAIR post–contrast-enhanced image (B.a) MRI from 3 patients with AQP4-IgG–positive NMOSD (A, B, and C) during attacks, showing leptomeningeal enhancement (A.a, A.b, B.a, C.a, and C.b), marked with arrows. Parenchymal lesions are seen including cloud-like enhancement (B.c, A.c, and C.c). Notably, enhancement occurred at the ependymal surface of the lateral ventricles (B.a). AQP4-IgG = aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G; FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; NMOSD = neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; T1W = T1 weighted.