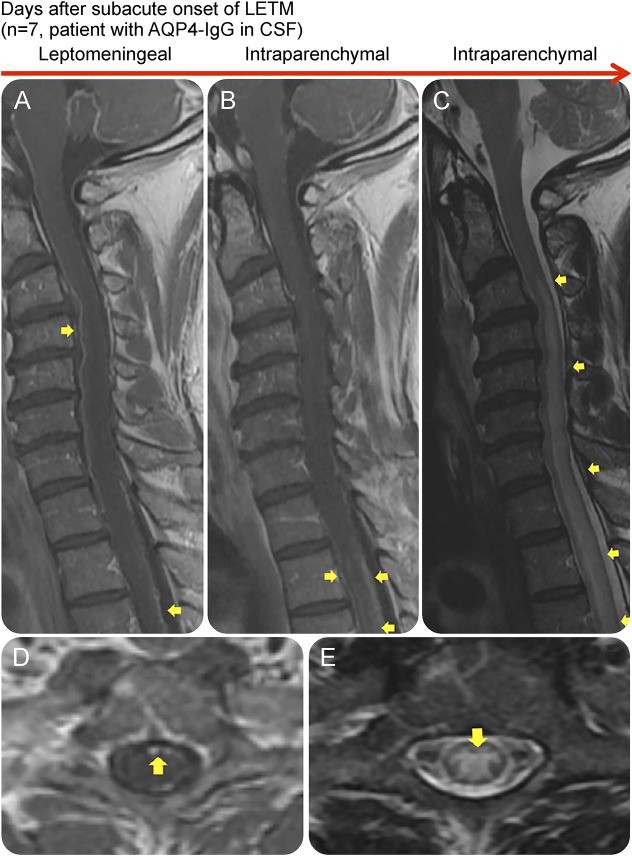
Figure 4. Leptomeningeal enhancement in association with the presence of AQP4-IgG in CSF and LETM.
Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1W (A and B), sagittal (C), axial (D), and axial (E) T2W MRIs of the spinal cord of an AQP4-IgG–positive NMOSD patient during attacks, showing leptomeningeal and intraparenchymal T1W contrast enhancement (A, B, and D). The spinal cord lesions were also demonstrated on T2W and STIR images (C and E). The patient had a subacute onset with atypical chest pain as the initial symptom, which after 7 days progressed to paraplegia and LETM on MRI. This patient was positive for AQP4-IgG in CSF. AQP4-IgG = aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G; LETM = longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis; NMOSD = neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; STIR = short tau inversion recovery; T1W = T1 weighted; T2W = T2 weighted.