Fig. 1.
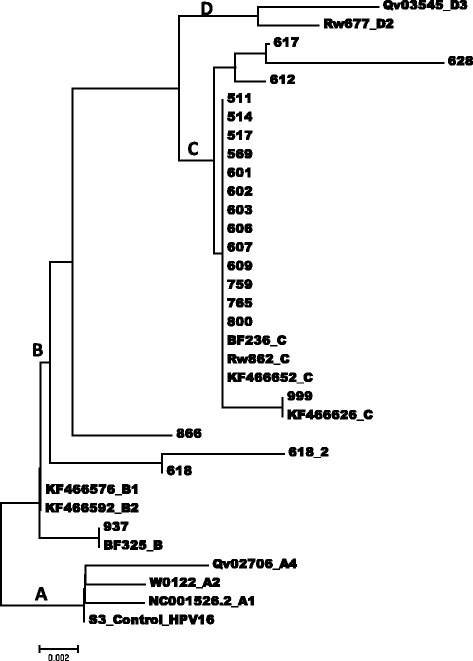
An evolutionary relationship of HPV16 isolates based on sequences between the genome positions 7469 and 7840 within the long control region (LCR.). The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbour-Joining method [37]. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 0.04170288 is shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method [38] and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The analysis involved 16 nucleotide sequences. Codon positions included were 1st + 2nd + 3rd + Noncoding. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 876 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA 6.0 [39]
