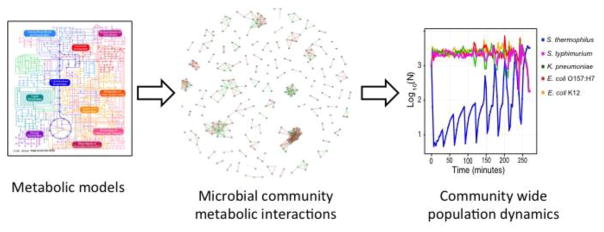
Figure 3. We argue that community metabolic models, which combine features of metabolic and ecological models, are needed to understand the mechanisms underlying community dynamics in the gut microbiome.
This type of modeling starts with a metabolic model for each organism within the community (left). These models are the used to generate an interaction matrix that contains a single net term for each pairwise microbe-microbe and microbe-host interaction (depiction of pairwise interactions between microbes, middle; green represents cooperative interactions, red represents competitive interactions). This matrix is then used to parameterize an ecological model, which can be used to predict how manipulating specific aspects of the microbiome—with probiotics, prebiotics, or nutritional interventions, for example—will affect properties such as stability and resilience.