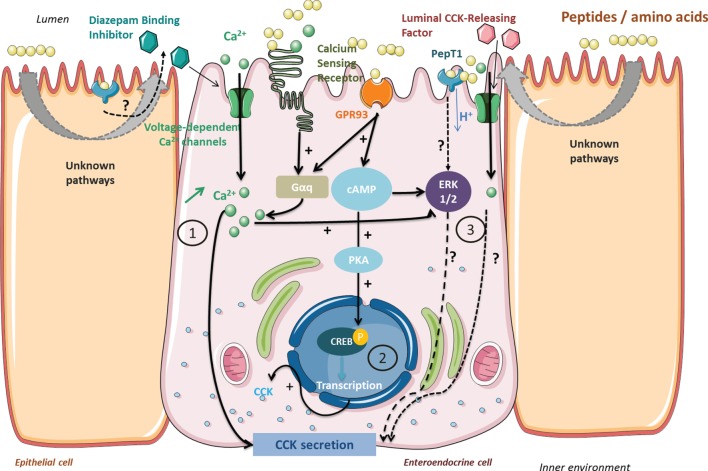
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways activated by peptides and amino acids involved in cholecystokinin (CCK) secretion and synthesis in enteroendocrine cells. Peptides from protein gastrointestinal digestion released in the lumen stimulate CCK secretion via (1) calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) or GPR93 activation causing an intracellular Ca2+ increase. Voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels enable an extracellular Ca2+ uptake when activated by CaSR and GPR93 or by membrane depolarization following dipeptide transport by PepT1. GPR93 activation by peptides may initiate CCK gene transcription (2) by ERK 1/2 or phosphokinase A signaling pathway activation. Other pathways are still investigated (3) and might indirectly imply PepT1 or luminal CCK-releasing factor in CCK secretion.