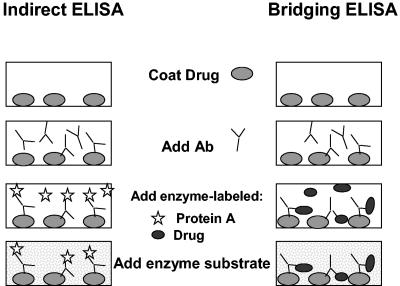
FIG. 1.
Schematic illustrations of indirect and bridging ELISA testing procedures for measuring Abs against protein drugs (e.g., EPO). In the indirect ELISA, the protein drug is coated onto the wells of plastic assay plates prior to the addition of serum samples. Any specific Abs that are bound to the immobilized protein are subsequently detected with enzyme-linked, anti-Ig Abs (monoclonal or polyclonal) and enzyme substrate. In the bridging ELISA shown here, the unlabeled protein drug is first coated onto the wells, serum Abs are allowed to bind to the immobilized drug, and Abs are then detected with enzyme-labeled drug plus enzyme substrate. The bridging ELISA depicted here relies on the ability of bivalent Abs (IgG) to bridge the immobilized drug with enzyme-labeled drug in solution.