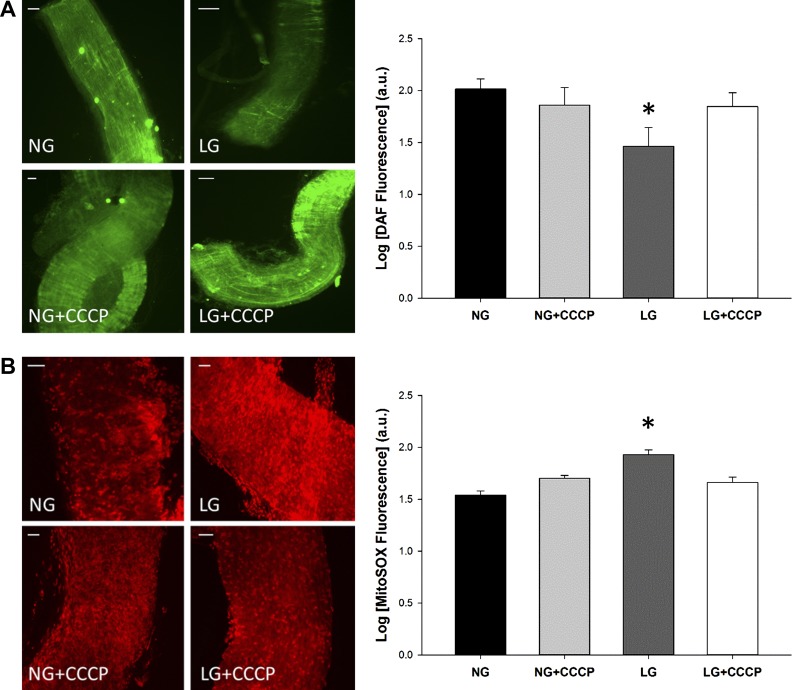
Fig. 5.
Mitochondrial membrane depolarization improves bioavailability of NO and reduces mitochondrial superoxide in isolated arterioles. A: vessels were incubated with DAF-2DA with or without exposure to carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazine (CCCP) (100 nmol/l), a membrane depolarizing agent. LG-treated vessels displayed a significant decrease in NO level compared with other treatment groups (P = 0.003 overall, *P < 0.03 for LG vs. all other exposures, N = 5), while membrane depolarization with CCCP increased NO levels approximating that of the NG+CCCP group. B: superoxide was detected with MitoSOX in the presence of CCCP (100 mol/l). LG-treated vessels displayed a significant increase in superoxide compared with other treatment groups based on increased fluorescence, while membrane depolarization with CCCP decreased MitoSox fluorescence (P < 0.001 overall, *P < 0.01 for LG vs. all other exposures, N = 4). Scale bars represent 50 μm.