Figure 1.
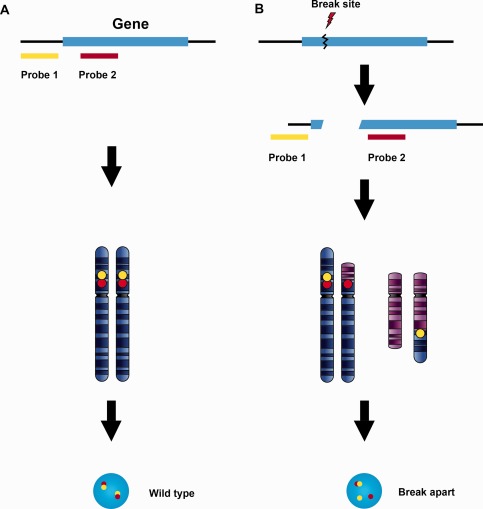
Break‐apart probe design for translocations with multiple fusion partners. A break‐apart probe set is composed of two probes specific for loci physically close to each other on the chromosome in their wild type configuration. The wild type signal pattern shows two pairs of closely approximated or fused signals (A). When translocation occurs involving a breakpoint between the two probe sites, the originally juxtaposed loci (fusion signals) split apart (B). The beauty of this design is that it detects chromosomal translocation regardless of the fusion partner involved. However, the break‐apart probe only identifies the breaking away of a gene fragment from its original location. It does not determine which chromosome receives the fragment or which genes may serve as fusion partners in the new location.
