Figure 4.
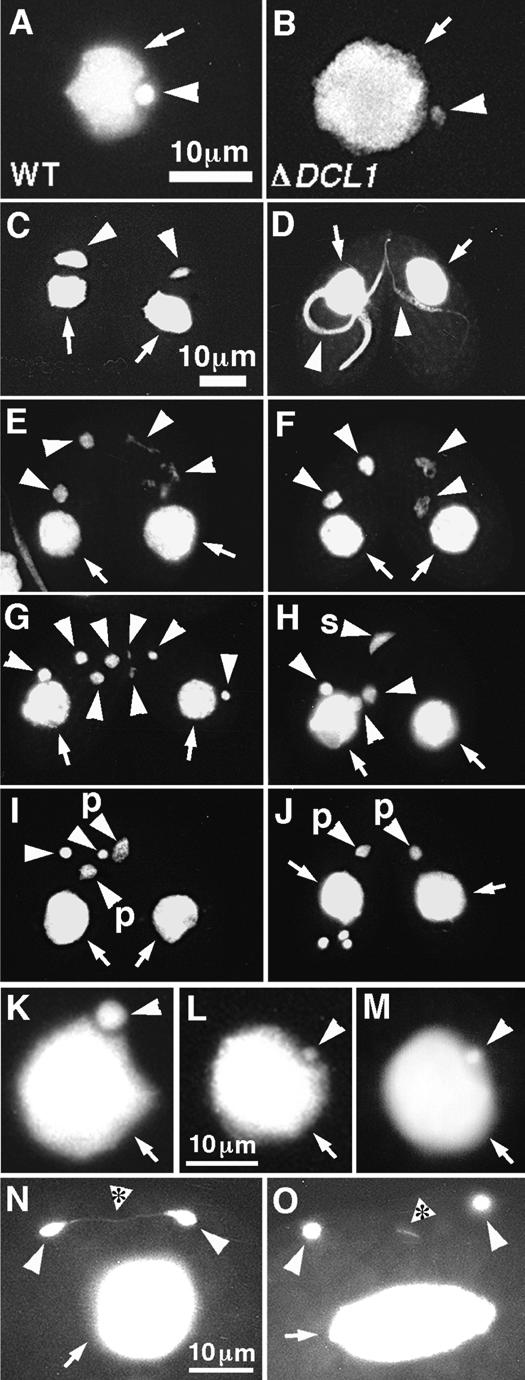
DCL1 is required for Mic chromosome maintenance. (A,B) Comparison of wild-type (A) and DCL1 knockout (B) cells. The log-phase growing cells were fixed and stained with DAPI. The Mics in DCL1 knockout cells contain much less DNA than those of wild-type cells. A and B share the same scale bar shown in A.(C–J) The Mics of DCL1 knockout cells cannot transmit genetic material to the next generation. Wild-type cells and DCL1 knockout cells were crossed, and the fixed cells were stained with DAPI. Mic abnormalities suggest that wild-type and DCL1 knockout cells were at left and right, respectively. Cells were in stages of early crescent (meiotic prophase; Stage II) (C), late crescent (meiotic prophase; Stage IV) (D), first meiotic division completed (E,F), second meiotic division completed (G), prezygotic mitosis (H), pronuclear (unilateral) exchange (I), and pronuclear (unilateral) exchange completed (J). For stages, see Sugai and Hiwatashi (1974) and Cole et al. (1997). The Macs and the Mics are marked with arrows and arrowheads, respectively. In H, the selected, mitotically dividing haploid Mic is marked with an s, and in I and J, pronuclei are marked with a p. C–J share the same scale bar shown in C. (K,L) A DCL1 knockout RI strain loses Mic chromosomes during vegetative growth. DCL1 knockout RI cells (ΔDCL1-14A-RI) were fixed at about 12 (K) and 60 (L) fissions after Round I genomic exclusion and stained with DAPI. (M) A DCL1 somatic knockout strain loses Mic chromosomes. DCL1 somatic knockout cells in interphase were fixed and stained with DAPI. K–M share the same scale bar shown in L. (N,O) DCL1 knockout cells show lagging chromosomes during Mic mitosis. DCL1 knockout RI cells in late stages of Mic mitosis were fixed and stained with DAPI. Two daughter Mics were often connected by DNA (N, arrowhead with asterisk); what appear to be chromosomes or chromosome fragments were often left between the daughter Mics (O, arrowhead with asterisk). N and O share the same 10-μm scale bar shown in N. In all pictures, the Macs and the Mics are marked with arrows and arrowheads, respectively.
