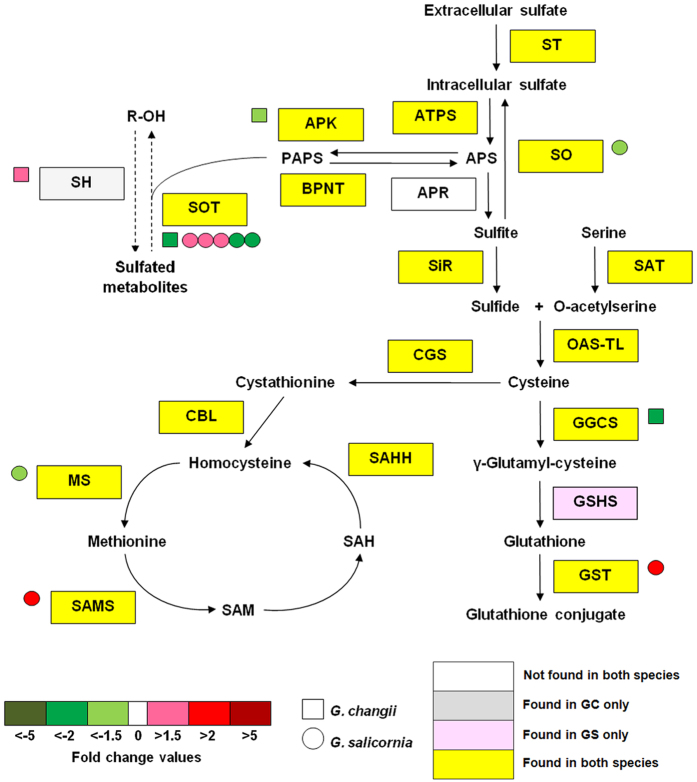
Figure 5. Effects of sulfate deprivation on the expression level of genes involved in sulfur metabolism.
The sulfur metabolism pathway was modified from Takahashi et al.2. Each square and round box represents an unigene from G. changii (GC) and G. salicornia (GS), respectively. Yellow and white rectangles indicate transcripts that are found to be present or absent in the transcriptomes of both Gracilaria species, respectively, whereas grey and pink rectangles indicate transcripts that are only present in G. changii and G. salicornia, respectively. Dotted lines indicate enzymatic reaction encoded by unknown gene(s) from a gene family. All expression values are based on the biological averaging of pooled samples from three individual plants. APS, adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; APK, APS kinase; APR, APS reductase; ATPS, ATP sulfurylase; BPNT, 3′(2′), 5′-bisphosphate nucleotidase; CBL, cystathionine beta-lyase; CGS, cystathionine gamma-lyase; GGCS, γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase; GSHS, glutathione synthetase; GST, gluthathione-S-transferase; MS, methionine synthase; OAST-TL, O-acetylserine (thiol)-lyase; PAPS, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAHH, SAH hydrolase; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAMS, SAM synthethase; SAT, serine acetyltransferase; SH, sulfohydrolase/sulfurylase; SiR, sulfite reductase; SO, sulfite oxidase; SOT, sulfotransferase; ST, sulfate transporter/permease.