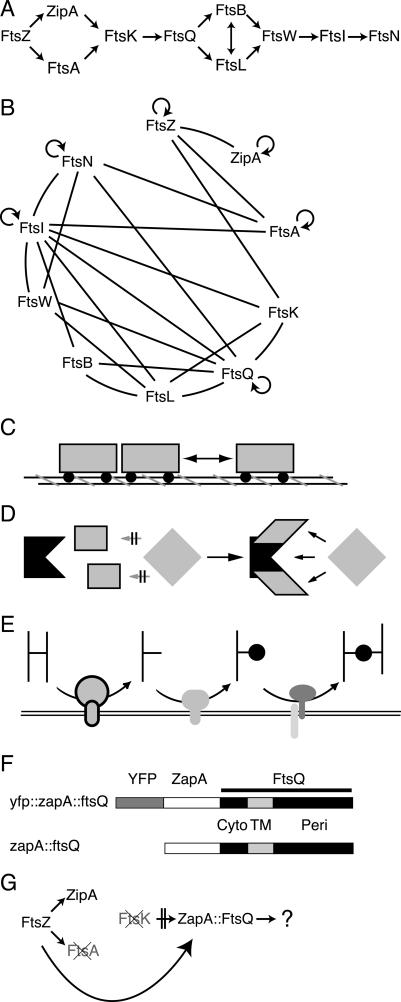
Figure 1.
(A) The septal recruitment pathway for cell division proteins in E. coli. (B) Bacterial two-hybrid results summarized from several groups (Di Lallo et al. 2003; G. Karimova and D. Ladant, in prep.; M. Gonzalez and J. Beckwith, unpubl.). Cell division proteins are listed clockwise corresponding to their respective order in A. Lines indicate proposed interactions; circular arrows indicate proposed homodimerization. (C–E) Potential models for divisome assembly. (C) Linear assembly. (D) Cooperative binding by an upstream complex. (E) Sequential activities plus substrate recognition. (F) ZapA–FtsQ constructs used in this work. (Cyto) Cytoplasmic domain of FtsQ; (TM) transmembrane segment of FtsQ; (Peri) periplasmic domain of FtsQ. YFP and non-YFP constructs are identical except for the addition of YFP fused in frame to the N terminus of ZapA. (G) Proposed premature targeting of ZapA–FtsQ construct.