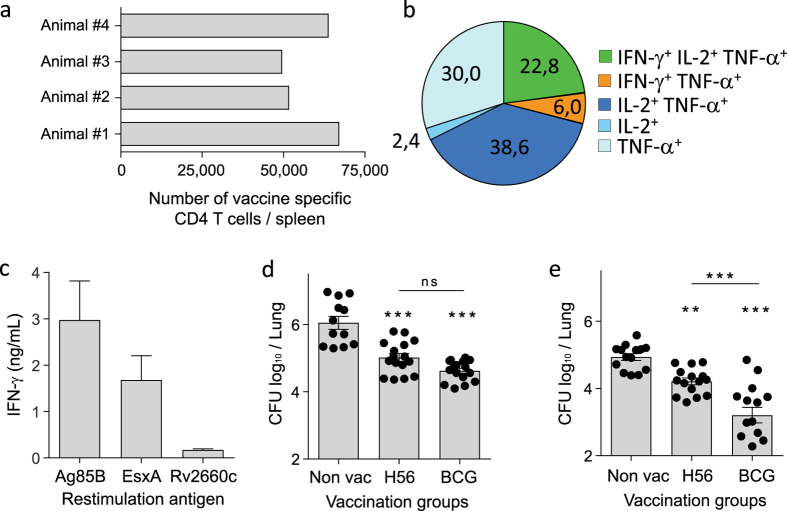
Figure 2. Strong H56 vaccine-take only induces moderate protection against the M.tb DK9897 strain.
(a) The number of vaccine-specific CD4 T cells was measured by flow cytometry in splenocytes 3 weeks after third vaccination. CD4 T cells that after re-stimulation with a cocktail of H56 single proteins (Ag85B + EsxA + Rv2660c) produced at least one of the cytokines, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2 or IL-17 were scored as vaccine specific. Results from four individual mice are shown. (b) The same spleen cells were used to investigate the polyfunctionality of the H56 specific T cells by measuring the frequencies of the seven possible combinations of TNF-α, IFN-γ and/or IL-2 producing T cells after stimulation with H56 proteins. The pie shows an average of the four animals. (c) The ability of CD4 T cells isolated from vaccinated mice (n = 4) to recognize the three single proteins in the H56 fusion protein was measured as IFN-γ release after restimulation with either Ag85B, EsxA or Rv2660c protein. (d,e) Bacterial load in individual lungs six weeks after aerosol infection with M.tb Erdman (d) or M.tb DK9897 (e), respectively. Measured by plating serial dilutions of lung homogenate and counting the number of mycobacteria after incubation. Combined results from two independent experiments are shown. Mean values and SEM’s are indicated. Statistical analysis, One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, ns = non-significant.