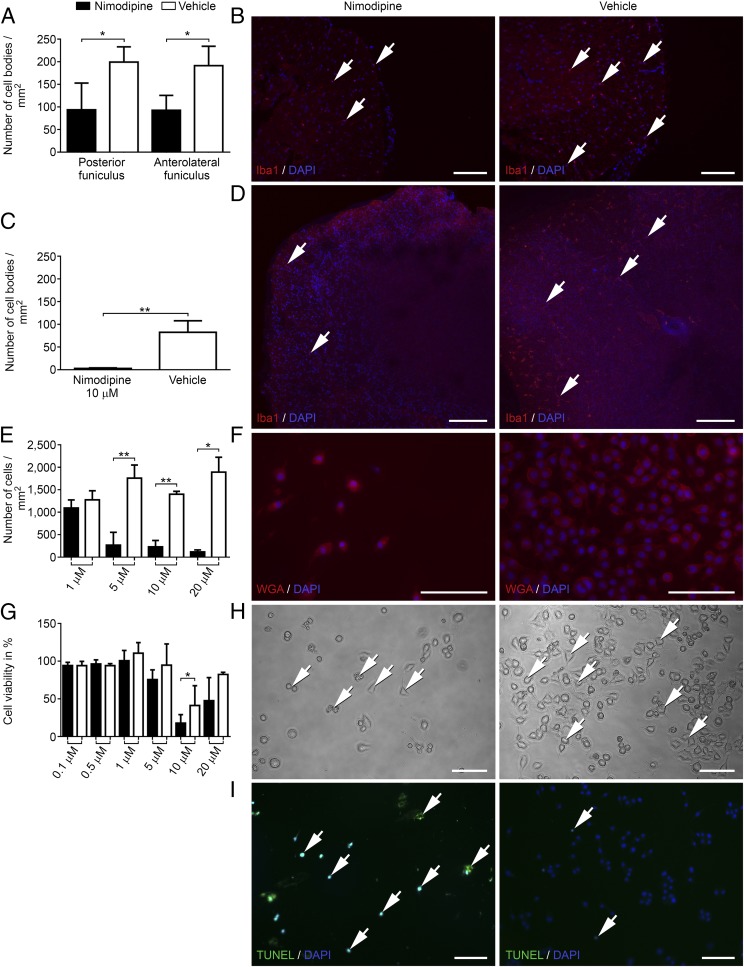
Fig. 3.
Nimodipine treatment leads to shrinkage, rounding, and apoptosis of microglial cells as well as significantly decreased numbers of Iba1+ cells in murine spinal cord and organotypic spinal cord culture. (A) Number of Iba1+ cell bodies/mm2 in the spinal cord of animals with EAE. (B) Nimodipine treatment (n = 4) compared with vehicle-treated mice (n = 3). (C and D). Organotypic slice cultures after treatment with 10 µM nimodipine (n = 4) or vehicle (n = 3) for 24 h. (E and F) Number of WGA-stained cells/mm2. (G) Viability of N9 cells after treatment with 10 µM nimodipine for 24 h as measured by MTT assay. (H) Representative cell-culture images. Arrows indicate cells that display rounding, shrinkage, and pathological vesicles. (I) Apoptosis was visualized by TUNEL assay. Arrows indicate positive cells in the respective panels. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01 by two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. Cell-culture data were obtained from at least three independent experiments. (Scale bars: 100 µm.)