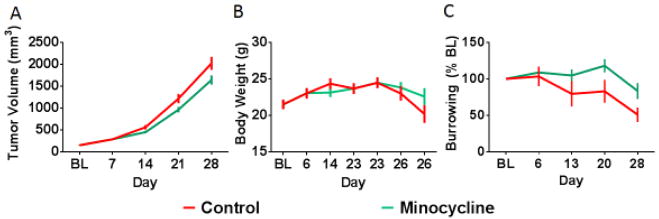
Fig 4.
Tumor growth and burrowing deficits are attenuated by minocycline treatment. Minocycline treatment resulted in a mild reduction in rate of tumor growth reaching significance on day 21 (A). There was no significant effect of minocycline on body weight (B). Minocycline treatment also significantly attenuated tumor-induced burrowing deficits with effects emerging on day 20 and 28 (C). Two mice, one from each group, required early termination due to rapid tumor growth; missing data values (for day 26/28) were replaced with group means to allow for repeated measures analyses. n=10 mice/group. * p<0.05