Fig. 1.
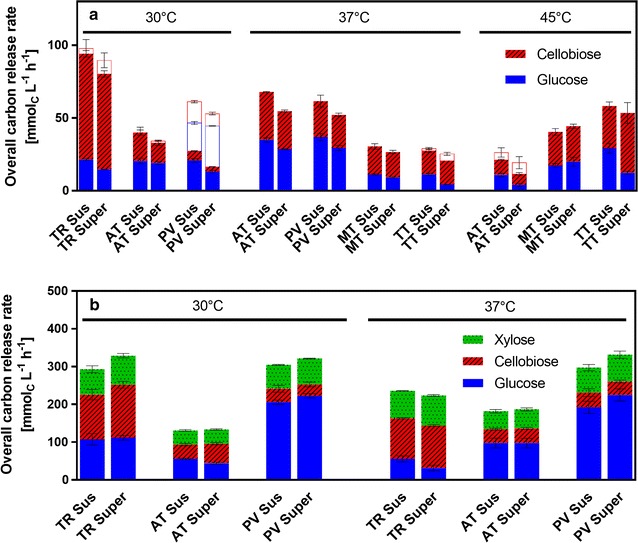
Cellulase activity screening of five candidate organisms cultivated under different conditions evaluated by the freeze assay. Freeze assay was performed at the indicated cultivation temperature with either suspended full culture broth (“sus,” first stacked bar) or supernatant (“super,” second stacked bar). Bars show overall carbon release rate as a sum of glucose, cellobiose and xylose carbon release rate. Colors indicate the distribution of these sugars. Error bars show standard deviation of biological triplicates. TR, Trichoderma reesei; AT, Aspergillus terreus; PV, Penicillium verruculosum; MT, Myceliophtora thermophila; TT, Thielavia terrestris; a Preliminary cellulase activity screening at a cultivation temperature of 30, 37, and 45 °C: cellulase activity was measured after 3 days of cultivation in non-buffered medium with 7.5 g L−1 avicel. Freeze assay was performed with avicel measuring glucose and cellobiose. Ghost bars show activity values measured after 10 days of cultivation in cases where maximum activity was not reached after 3 days. b Refined cellulase activity screening at a cultivation temperature of 30 and 37 °C: cellulase activity was measured after 5 days of cultivation in 0.1 M PIPPS buffered medium with 5 g L−1 glucose and 30 g L−1 α-cellulose. Freeze assay was performed with α-cellulose measuring glucose, cellobiose, and xylose. Assay conditions: 91 mM itaconic acid buffer (pH 3.7), 120 g L−1 cellulose, incubation time 2 h, filling volume 1.1 in 2-mL test tube, shaking frequency 900 rpm, shaking diameter 3 mm
