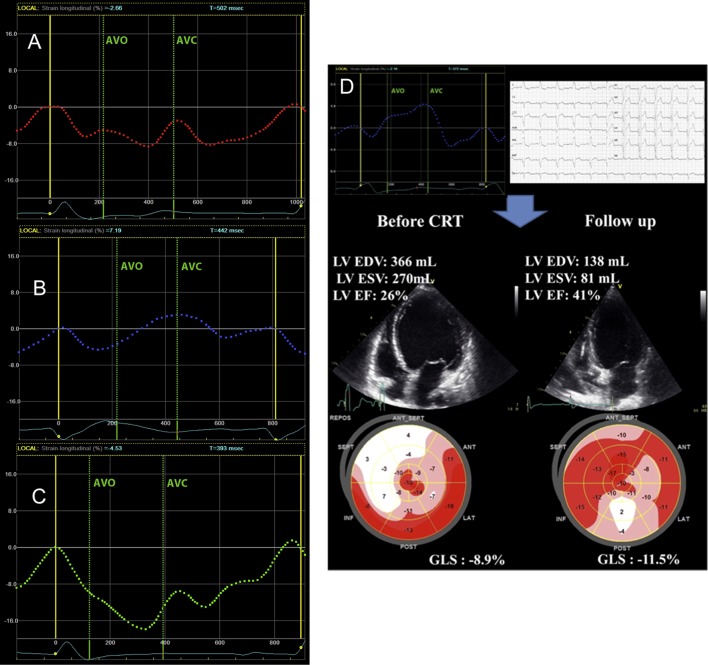
Figure 3.
(A) Characterisation of LV septal deformation patterns using speckle-tracking longitudinal strain. Double-peaked systolic shortening (A, pattern 1), early pre-ejection shortening peak followed by prominent systolic stretch/lengthening (B, pattern 2) and pseudonormal shortening with a late-systolic shortening peak and less pronounced end-systolic stretch (C, pattern 3). Patterns 1 and 2 are associated with better improvement in echocardiographic outcomes and event-free survival post-CRT compared with pattern 3. (D) Example of a patient with severe heart failure, LBBB (QRS width 180 ms) and septal deformation pattern 2. Response to CRT with reduction in LV volumes and improvements in LV function and GLS is demonstrated. Reprinted from Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography, Vol 27, Marechaux S, Guiot A, Castel AL, Guyomar Y, Semichon M, Delelis F, Heuls S, Ennezat PV, Graux P & Tribouilloy C, Relationship between two-dimensional speckle-tracking septal strain and response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with left ventricular dysfunction and left bundle branch block: a prospective pilot study, pp 501–511, Copyright (2014) American Society of Echocardiography, with permission from Elsevier.

 This work
is licensed under a
This work
is licensed under a