Figure 7.
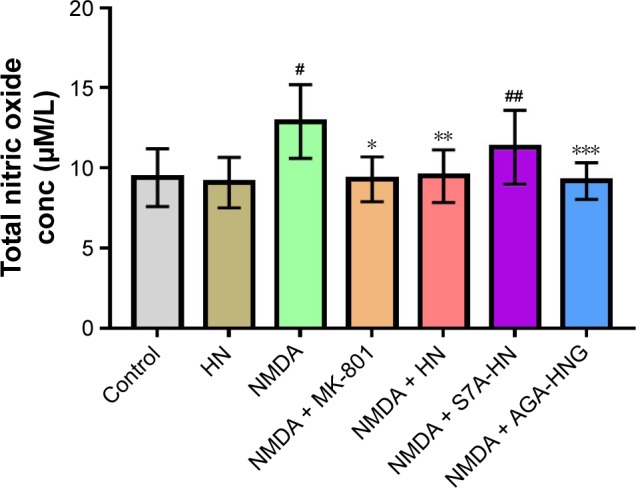
Effect of HN on NMDA-induced nitric oxide production.
Notes: Data are shown as mean ± SD (n=5). Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. #Control group versus NMDA group, P=0.000; *NMDA versus NMDA + MK-801, P=0.003; **NMDA versus NMDA + HN, P=0.002; ##control versus NMDA + S7A-HN, P=0.004; ***NMDA versus NMDA + AGA-HNG, P=0.005. NMDA: 100 μmol/L; MK-801: 10 μmol/L; MK-801: 10 μmol/L; HN, S7A-HN, and AGA-HNG: 1 μmol/L each. NMDA is an excitotoxin that induces the overactivation of NMDA receptor, causing excitotoxicity. MK-801 is a known uncompetitive antagonist of NMDA receptor, which could block the binding of NMDA.
Abbreviations: AGA-HNG, 100× more active form of HN; ANOVA, analysis of variance; conc, concentration; HN, humanin; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; S7A-HN, inactive form of HN; SD, standard deviation.
