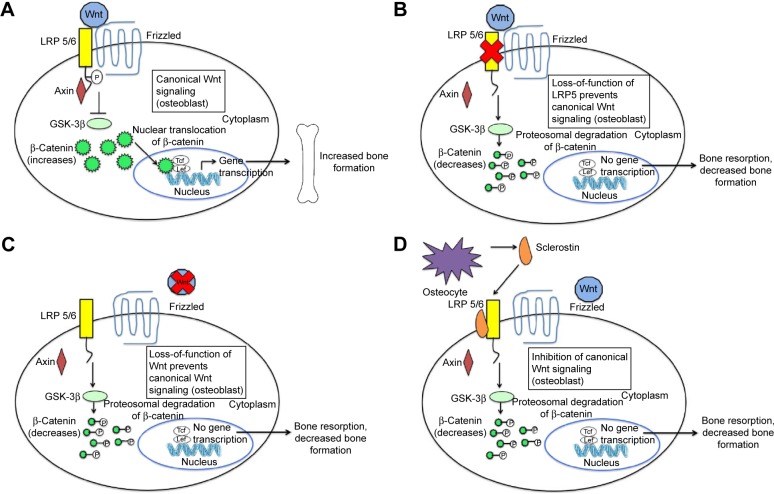
Figure 1.
The canonical Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway and the effects of inhibition through loss of function mutations and sclerostin inhibition.
Notes: (A) When Wnt binds to the LRP-5 and -6 coreceptors and the specific Frizzled family receptor, inhibition of the β-catenin destruction complex occurs. Accumulated β-catenin in the cytoplasm enters the nucleus, leading to transcription of Wnt-responsive genes and bone formation. Panels (B), (C), and (D) show how various mechanisms inhibit the canonical Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway. Due to the inability of Wnt to exert its effect due to (B) the loss of mutation of LRP-5 and LRP-6 coreceptors, (C) the loss of mutation of Wnt, and (D) the prevention of Wnt from binding to LRP-5 or LRP-6 coreceptors by sclerostin, the β-catenin destruction complex is assembled. β-Catenin is phosphorylated and degraded. Wnt-responsive genes are not activated, leading to an increased bone resorption and a decreased bone formation. Copyright ©2015. Dove Medical Press. Shah AD, Shoback D, Lewiecki EM. Sclerostin inhibition: a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of osteoporosis. Int J Womens Health. 2015;7:565–580.7
Abbreviation: LRP, LDL-receptor-related protein.