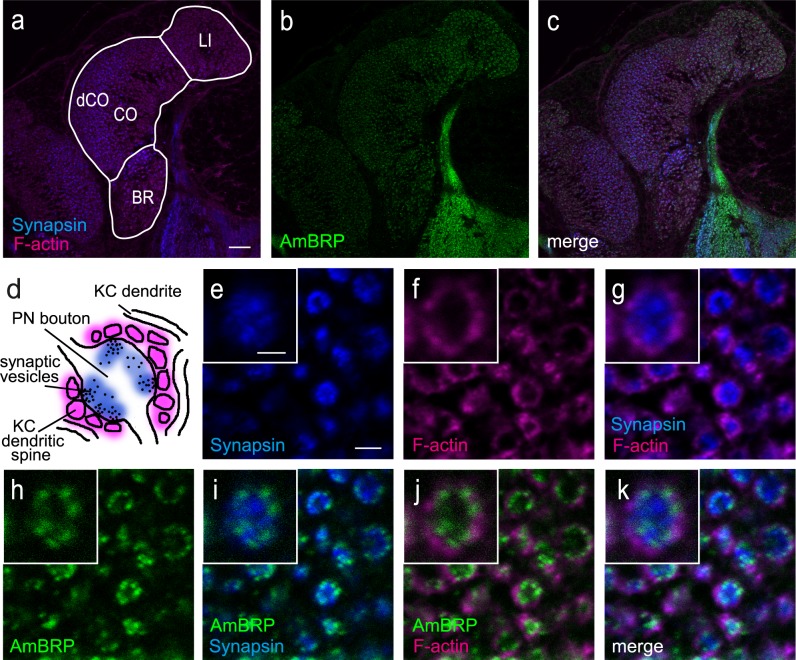
Fig 3. AmBRP is predominantly located in the vicinity of the membrane of presynaptic boutons within microglomeruli in the mushroom body calyces.
a-c Confocal images of the medial calyx showing BRPlast200 staining (AmBRP, green, b) in combination with Phalloidin staining (F-actin, magenta, a) and an anti-SYNORF1 counterstaining (Synapsin, blue, a) to visualize pre- and postsynaptic structures in a 8-day-old bee. The calyx can be subdivided into three regions, lip, collar and basal ring. Experiments focused on the lip and the dense region of the collar (dCO). d Schematic representation of a microglomerulus (MG) (modified after [35] showing already established pre- and postsynaptic marker (Synapsin, blue; F-actin, magenta). The bouton of a projection neuron is surrounded by spines from Kenyon cell dendrites. Anti-SYNORF1 labels the vesicle-associated protein Synapsin (blue) whereas Alexa Fluor 546 Phalloidin binds to F-actin located in dendritic spines (magenta). e-k Confocal images of MG in the dense collar region with labeled Synapsin (e), F-actin (f) and AmBRP (h). The F-actin signals form circles around Synapsin signals (g). AmBRP is located predominantly at the outer rim of the Synapsin-labeled signals and at the inner rim of the F-actin signals (i-k). The insets show a single, magnified MG from the corresponding image. LI, lip; CO, collar; BR, basal ring; dCO, dense collar; PN, projection neuron; KC, Kenyon cell.Scale bars: 20 μm for a-c, 2 μm for e-k, 1 μm for insets.