Fig 6. C15 and Dll interact functionally.
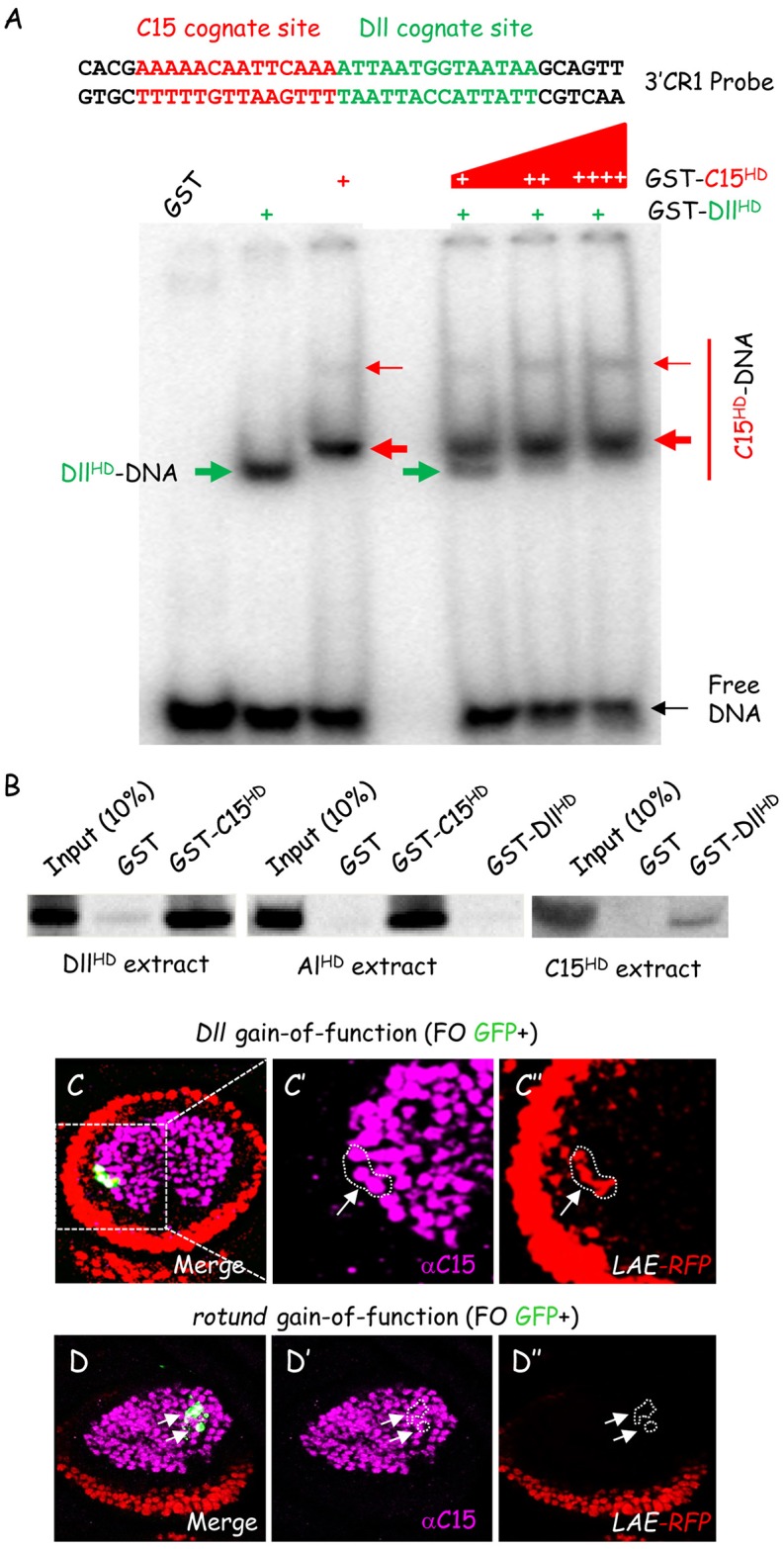
(A) C15 and Dll outcompete for CR1 binding. EMSA was done with a probe encompassing the DBS and the neighboring S6 C15 binding site (CR1 3’ half; upper panel). DllHD and C15HD GST fusions were tested in isolation or together with increasing amount of purified GST-C15HD. No heterodimeric C15-Al DNA complex could be detected. Moreover, GST-DllHD binding was abolished in a dose-dependent manner in favor of GST-C15HD. (B) Pull-down experiments with purified GST-C15HD or GST-DllHD fusions and in vitro translated C15, Dll or Al HD. (C-D) Mosaic late L3 leg discs expressing the LAE-RFP reporter and harboring FO clones (GFP positive) (circled with white dashed lines) misexpressing C15 (C) or Rn (D) proteins. Merged LAE-driven RFP fluorescence (red) and C15 immunostaining (magenta) are shown, as well as each marker in isolation, in (C’–C”) and (D’-D”), respectively. Note that LAE-RFP is specifically de-repressed in Dll overexpressing FO clones without detectable change in C15 expression.
