Figure 1.
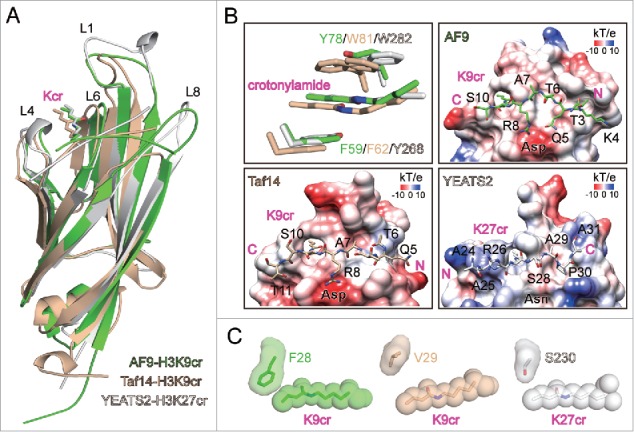
Molecular details of crotonyllysine recognition by YEATS domains. (A) Superimposition of AF9-H3K9cr, Taf14-H3K9cr, and YEATS2-H3K27cr complex structures. YEATS proteins and H3 peptides are depicted as cartoon, with sidechains of crotonyllysine shown as sticks. The color code is given in the bottom-right corner, and the same code is applied throughout the entire figure. (B) Aromatic-π-aromatic stacking and electrostatic potential surfaces ranging from −10 to +10 (kT/e) of AF9, Taf14, and YEATS2 YEATS domains. Key aromatic residues, crotonyllysine sidechains, and H3 peptides are shown as sticks. Oxygen atoms: red; Nitrogen atoms: blue. The W81 side chain of Taf14 is shown in dual conformation. (C) Relative positions of space-filling crotonyllysine and adjacent loop 1 residue in AF9, Taf14, and YEATS2 YEATS domain structures.
