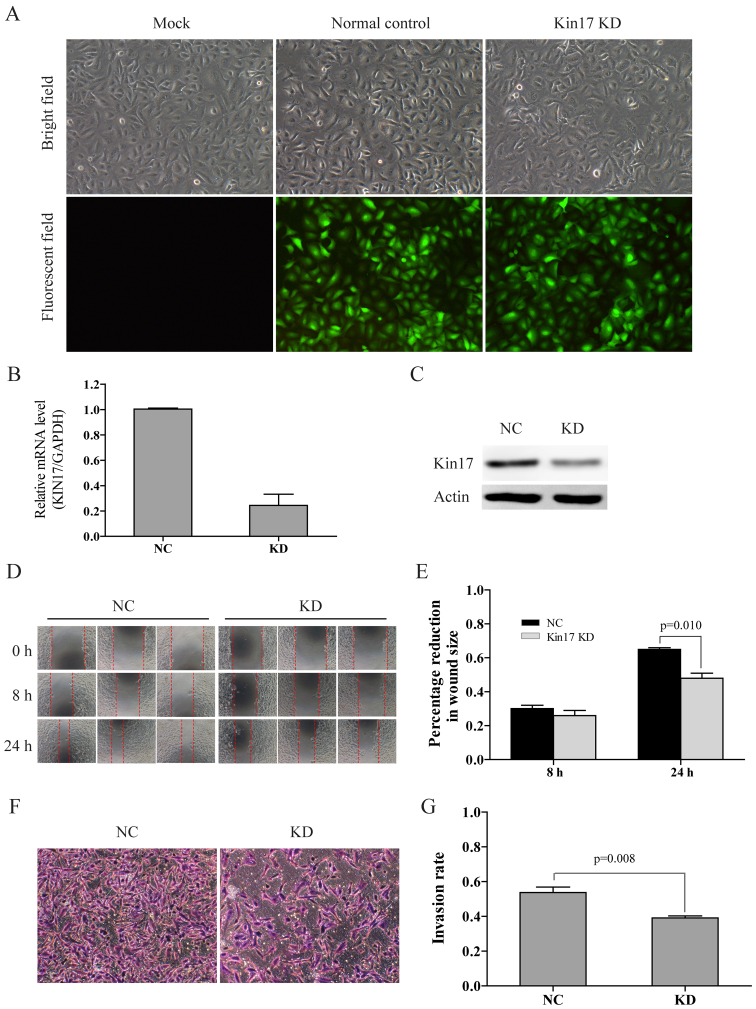
Figure 2.
Knockdown of KIN17 by lentiviral recombinant vector-mediated siRNA transfection inhibited the invasiveness of A549 cells. (A) Morphological features and fluorescence-indicated transfection of A549Mock, A549NC and A549KIN17 KD cells (×100). (B) mRNA and (C) protein levels of KIN17 in A549NC and A549KIN17 KD cells were decreased following KIN17 knockdown, identified by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis and western blotting, respectively. Scratch assay (D) representative images (×100) and (E) quantification. Matrigel assay (F) representative images (×100) and (G) quantification. KIN17, KIN17 DNA and RNA binding protein; A549KIN17 KD, A549 cells transfected with recombinant lentiviral vectors carrying the KD4 siRNA sequence targeting KIN17 gene; A549NC, A549 cells transfected with the control vector; A549MOCK, A549 cells without transfection of vector.