Abstract
A 72-year-old female was referred for further evaluation of epigastralgia. Abdominal contrast computed tomography revealed numerous tumors in the two lobes of the liver. Liver biopsy and immunohistochemical staining revealed that the tumor cells were positive for factor VIII-associated antigen, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 and human hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen, concordant with a diagnosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEH). To elucidate the etiology of HEH, particularly the microRNA (miRNA) profiles, tissue samples obtained from normal and tumor tissues were analyzed using a miRNA array system. A total of 14 miRNAs were significantly upregulated and 93 miRNAs were downregulated in the tumor tissues (P<0.01). Additionally, unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis using Pearson's correlation revealed that the tumor tissues clustered separately from the normal tissues. The miRNA expression profile was analyzed in HEH and compared with angiosarcoma, which exhibits histology similar to HEH. Out of a total of 107 miRNAs, only miR-122-5p and miR-1290 demonstrated a differential expression pattern in angiosarcoma. Therefore, these miRNAs may be novel biological markers for the determination of a diagnosis of HEH in primary mesenchymal tumors of the liver. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first report of a miRNA microarray analysis in HEH.
Keywords: microRNA profile, hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, angiosarcoma, hemangioma, multiple liver tumors
Introduction
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a rare disease that was initially described by Weiss and Enzinger in 1982 (1). EHE develops from a malignant transformation of the vascular endothelium and is generally located in soft tissues and internal organs (1). Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEH) is the most common type of EHE; forms of EHE in other organs, including the lungs, brain, spleen, bones, breast, heart and stomach have been reported only rarely (2–6). HEH is a rare sarcoma of the liver, which typically presents as a number of nodules and may be misdiagnosed as a metastatic carcinoma (7,8). Additionally, HEH may recur locally and metastasize to distant organs (8); HEH has previously been considered an intermediate malignancy (9). However, the World Health Organization has previously categorized EHE as having full malignant potential (10). Therefore, it is crucial to identify the grade of malignancy and to distinguish HEH from other types of epithelioid vascular tumors, including epithelioid hemangioma and epithelioid angiosarcoma. However, due to the morphological similarities, it is challenging to differentiate these tumors solely using histological features (7). The current study focused on microRNAs (miRNAs) and performed miRNA profiling, in order to identify novel specific biomarkers for the accurate diagnosis of HEH.
Case report
A 72-year-old female was referred to Kagawa University Hospital in 2014 (Kagawa, Japan) for further evaluation of epigastralgia. The patient had no significant medical history and no familial history of genetic disorders or cancers. Abdominal contrast computed tomography (CT) revealed a number of liver tumors (Fig. 1A); multiple nodules with capsules located peripherally in the liver were apparent, with coarse calcification and peripheral enhancement following the administration of contrast medium. A liver biopsy and immunohistochemical staining revealed that the tumor cells were positive for factor VIII-associated antigen (FVIII-rAg), platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD31) and human hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen (CD34), consistent with a diagnosis of HEH (Fig. 1B). Primary antibodies against human FVIII-rAg (Dako, Tokyo, Japan), CD31 (Dako, JC70A, Tokyo, Japan), and CD34 (Leica Microsystems, Tokyo, Japan) were added to paraffin-embedded liver sections. Secondary antibodies, including ImmPRESS™ REAGENT Anti-Rat Ig and ImmPRESS™ REAGENT Anti-Rabbit Ig, were also used (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA) and incubated with a DAB Substrate kit (Vector Laboratories, Inc.).
Figure 1.
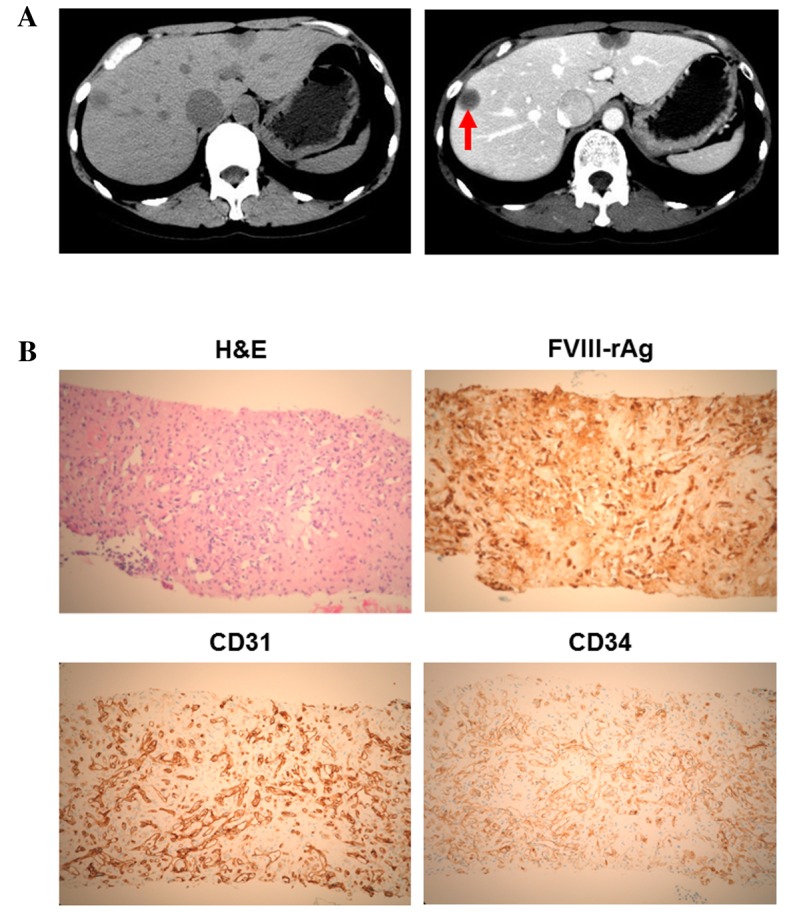
Clinicopathological features of the present case of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. (A) Computed tomography revealed hypodense tumors in the two lobes (left panel). In the portal phase, the center of the tumor was enhanced in the right lobe (right panel; red arrow). (B) In the H&E-stained section, tumor cells were observed to form intracytoplasmic lumina, and solitary, alveolar and single-file patterns were detected. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that the tumor cells were positive for FVIII-rAg, CD31 and CD34. FVIII-rAg, factor VIII-associated antigen; CD31, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; CD34, human hematopoietic progenitor cell antigen; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.
The patient was treated with a partial ultrasonography-guided hepatectomy for the multiple HEHs. Currently the patient is still alive and has been relapse-free for 2 years post-surgery.
To elucidate the etiology of HEH, particularly the miRNA profiles, tissue samples obtained from three separate sections of normal and tumor tissues were analyzed. Total RNA was extracted from the human liver samples using the miRNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Inc., Venlo, Netherlands), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Following RNA measurement with an RNA 6000 Nano kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), the samples were labeled using a miRCURY Hy3 Power Labeling kit (Exiqon, Vedbaek, Denmark) and then hybridized onto a mouse miRNA Oligo chip (version 19; Toray Industries, Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Scanning was conducted with the 3D-Gene Scanner 3000 (Toray Industries, Inc.). The 3D-Gene extraction version 1.2 software (Toray Industries, Inc.) was used to read the raw intensities of the image. To determine changes in miRNA expression between normal tissue and tumor tissue samples, the raw data were analyzed via GeneSpringGX version 10.0 (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
A total of 14 miRNAs were significantly upregulated and 93 miRNAs were significantly downregulated in the tumor tissues, as compared with the normal tissues (Table I). Additionally, these data were organized using unsupervised hierarchical clustering and analysis of variance (ANOVA) functions in the GeneSpring software. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering was performed by using the clustering function (condition tree) with Pearson's correlation. Two-way ANOVA and asymptotic P-value computation without any error correction on the samples were performed to identify the miRNAs that varied most prominently across the different groups. The P-value cutoff was set as 0.05. In the present study, the miRNAs in tumor tissues clustered separately from those in normal tissues (Fig. 2). The microarray data used in the present study were submitted as a complete data set to the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (no. GSE66794). Each expression of 107 miRNAs, which were statistically up-and down-regulated in HEH tissues, was analyzed as compared to that profile in angiosarcoma which exhibits a similar histology to HEH by using ‘Sarcoma-microRNA Database’. The sarcoma miRNA expression database was accessed through http://www.oncomir.umn.edu/.
Table I.
Comparison of miRNAs between normal and HEH tumor tissues (P<0.01).
| A, Upregulated miRNAs | ||
|---|---|---|
| miRNA | P-value | Fold change (T/N), mean ± SD |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | 0.0059 | 26.4833±12.9514 |
| hsa-miR-155-5p | 0.0099 | 20.5192±8.659 |
| hsa-miR-181a-5p | 0.0071 | 13.1044±4.978 |
| hsa-miR-23b-3p | 0.0096 | 12.362±4.993 |
| hsa-miR-140-3p | 0.0076 | 12.7157±5.4437 |
| hsa-miR-125b-5p | 0.0056 | 11.0117±4.9514 |
| hsa-miR-4324 | 0.0096 | 10.1675±4.1997 |
| hsa-miR-214-3p | 0.0056 | 12.0701±7.5642 |
| hsa-miR-26a-5p | 0.0058 | 10.9722±5.6222 |
| hsa-miR-126-3p | 0.0064 | 8.2668±3.5601 |
| hsa-miR-130b-3p | 0.0074 | 8.3378±4.1174 |
| hsa-miR-6822-5p | 0.0055 | 7.8268±3.3700 |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | 0.0058 | 5.2697±1.8241 |
| hsa-miR-34c-3p | 0.0043 | 1.6188±0.1349 |
| B, Downregulated miRNAs | ||
| miRNA | P-value | Fold change (T/N), mean ± SD |
| hsa-miR-4463 | 0.0076 | 0.5185±0.1658 |
| hsa-miR-4713-5p | 0.0049 | 0.4745±0.1267 |
| hsa-miR-3191-5p | 0.0090 | 0.4616±0.1886 |
| hsa-miR-296-3p | 0.0059 | 0.441±0.1595 |
| hsa-miR-1290a | 0.0089 | 0.4589±0.1978 |
| hsa-miR-6716-5p | 0.0066 | 0.4225±0.1967 |
| hsa-miR-4442 | 0.0016 | 0.4199±0.1121 |
| hsa-miR-4534 | 0.0056 | 0.4224±0.1531 |
| hsa-miR-4484 | 0.0019 | 0.4176±0.1387 |
| hsa-miR-615-3p | 0.0065 | 0.3907±0.114 |
| hsa-miR-6791-5p | 0.0067 | 0.4044±0.1801 |
| hsa-miR-636 | 0.0006 | 0.3943±0.0982 |
| hsa-miR-6808-5p | 0.0076 | 0.4024±0.143 |
| hsa-miR-4800-3p | 0.0039 | 0.3808±0.1669 |
| hsa-miR-6855-3p | 0.0022 | 0.3805±0.1372 |
| hsa-miR-4525 | 0.0014 | 0.3655±0.0679 |
| hsa-miR-6165 | 0.0053 | 0.3614±0.1487 |
| hsa-miR-7114-5p | 0.0065 | 0.3395±0.128 |
| hsa-miR-6879-5p | 0.0012 | 0.3438±0.1193 |
| hsa-miR-3622a-5p | 0.0078 | 0.3342±0.1694 |
| hsa-miR-4497 | 0.0081 | 0.3358±0.1514 |
| hsa-miR-8089 | 0.0024 | 0.3367±0.1433 |
| hsa-miR-6880-5p | 0.0025 | 0.3261±0.1262 |
| hsa-miR-7854-3p | 0.0068 | 0.3168±0.1401 |
| hsa-miR-6895-5p | 0.0027 | 0.316±0.1378 |
| hsa-miR-885-5p | 0.0080 | 0.3281±0.1762 |
| hsa-miR-7110-5p | 0.0078 | 0.3198±0.1633 |
| hsa-miR-6877-5p | 0.0062 | 0.3072±0.1433 |
| hsa-miR-3194-5p | 0.0050 | 0.3039±0.1679 |
| hsa-miR-1469 | 0.0008 | 0.2858±0.1107 |
| hsa-miR-5010-5p | 0.0048 | 0.2964±0.1442 |
| hsa-miR-370-3p | 0.0043 | 0.2966±0.1479 |
| hsa-miR-4749-5p | 0.0099 | 0.3068±0.1709 |
| hsa-miR-6076 | 0.0084 | 0.2912±0.1304 |
| hsa-miR-664b-5p | 0.0081 | 0.2968±0.1903 |
| hsa-miR-4745-5p | 0.0043 | 0.276±0.0822 |
| hsa-miR-3714 | 0.0009 | 0.2668±0.0619 |
| hsa-miR-6824-5p | 0.0053 | 0.2791±0.0895 |
| hsa-miR-6825-5p | 0.0070 | 0.2823±0.1436 |
| hsa-miR-6889-5p | 0.0007 | 0.2673±0.1206 |
| hsa-miR-5585-3p | 0.0071 | 0.2779±0.1291 |
| hsa-miR-4428 | 0.0023 | 0.2574±0.1187 |
| hsa-miR-184 | 0.0069 | 0.2667±0.0888 |
| hsa-miR-642b-3p | 0.0068 | 0.2536±0.1318 |
| hsa-miR-3621 | 0.0014 | 0.2451±0.0755 |
| hsa-miR-6769a-5p | 0.0045 | 0.2436±0.1112 |
| hsa-miR-1247-3p | 0.0002 | 0.2335±0.0803 |
| hsa-miR-6757-5p | 0.0074 | 0.2381±0.1004 |
| hsa-miR-1233-5p | 0.0009 | 0.2357±0.0937 |
| hsa-miR-8060 | 0.0031 | 0.2276±0.0573 |
| hsa-miR-6825-3p | 0.0041 | 0.2303±0.0685 |
| hsa-miR-1254 | 0.0050 | 0.2409±0.1457 |
| hsa-miR-3925-5p | 0.0096 | 0.248±0.0242 |
| hsa-miR-6851-5p | 0.0047 | 0.2196±0.1064 |
| hsa-miR-6748-5p | 0.0081 | 0.2358±0.1399 |
| hsa-miR-4257 | 0.0071 | 0.2184±0.090 |
| hsa-miR-6743-5p | 0.0017 | 0.2173±0.0827 |
| hsa-miR-564 | 0.0020 | 0.2139±0.0959 |
| hsa-miR-8063 | 0.0060 | 0.2046±0.1137 |
| hsa-miR-1229-5p | 0.0044 | 0.2149±0.0950 |
| hsa-miR-6124 | 0.0072 | 0.2171±0.1188 |
| hsa-miR-4792 | 0.0006 | 0.1942±0.072 |
| hsa-miR-4476 | 0.0019 | 0.2045±0.0877 |
| hsa-miR-4481 | 0.0094 | 0.1983±0.0423 |
| hsa-miR-4435 | 0.0025 | 0.1843±0.0804 |
| hsa-miR-3150a-3p | 0.0043 | 0.1788±0.0622 |
| hsa-miR-122-5pa | 0.0094 | 0.1912±0.0978 |
| hsa-miR-6750-5p | 0.0097 | 0.1705±0.0376 |
| hsa-miR-4498 | 0.0011 | 0.1771±0.0938 |
| hsa-miR-6775-3p | 0.0038 | 0.167±0.0633 |
| hsa-miR-6870-5p | 0.0032 | 0.1774±0.0767 |
| hsa-miR-3682-3p | 0.0044 | 0.1664±0.0194 |
| hsa-miR-765 | 0.0033 | 0.1515±0.081 |
| hsa-miR-8071 | 0.0045 | 0.1602±0.0773 |
| hsa-miR-6782-5p | 0.0042 | 0.1646±0.0752 |
| hsa-miR-1236-5p | 0.0006 | 0.157±0.0564 |
| hsa-miR-7150 | 0.0022 | 0.161±0.0669 |
| hsa-miR-4756-5p | 0.0024 | 0.1585±0.081 |
| hsa-miR-6891-5p | 0.0073 | 0.1647±0.0828 |
| hsa-miR-4638-3p | 0.0009 | 0.1561±0.0716 |
| hsa-miR-6769b-5p | 0.0031 | 0.1561±0.0639 |
| hsa-miR-6871-5p | 0.0022 | 0.1439±0.0416 |
| hsa-miR-4443 | 0.0071 | 0.1427±0.0639 |
| hsa-miR-513a-5p | 0.0038 | 0.1287±0.0552 |
| hsa-miR-8078 | 0.0061 | 0.1079±0.0482 |
| hsa-miR-6842-5p | 0.0012 | 0.0943±0.0427 |
| hsa-miR-194-5p | 0.0015 | 0.0948±0.0434 |
| hsa-miR-6893-5p | 0.0045 | 0.0858±0.0367 |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | 0.0016 | 0.0816±0.0414 |
| hsa-miR-3162-5p | 0.0063 | 0.0799±0.0308 |
| hsa-miR-4450 | 0.0052 | 0.0558±0.0073 |
| hsa-miR-3678-3p | 0.0026 | 0.0546±0.0283 |
| hsa-miR-3649 | 0.0045 | 0.0417±0.0192 |
miRNAs were differentially expressed in angiosarcoma compared with HEH. miRNA, microRNA; HEH, hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma; T/N, tumor/normal tissue; SD, standard deviation.
Figure 2.
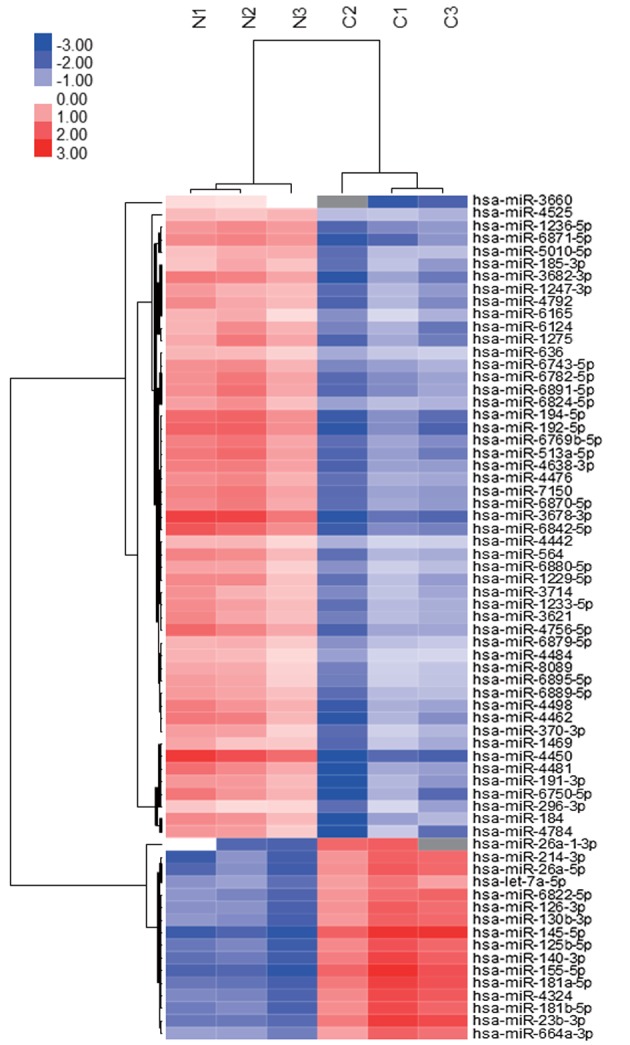
Hierarchical clustering of miRNAs between normal and tumor tissues. Liver tissue miRNA clustering was performed according to the expression profiles of 107 differentially expressed miRNAs between normal and tumor tissues. The analyzed tissue samples are presented in the columns and the miRNAs are presented in the rows. The miRNA-clustering tree is presented on the left and the sample-clustering tree is presented at the top. The color scale depicts the relative expression levels of the miRNAs in the patient tissue samples, with red representing a high expression level and blue representing a low expression level. miRNA, microRNA.
Of a total of 107 significantly upregulated and downregulated miRNAs identified in HEH, only miR-122-5p and miR-1290 demonstrated a differential expression pattern in angiosarcoma (Table I).
Discussion
HEH is a rare hepatic, vascular, soft-tissue tumor with malignant potential; the incidence of HEH is <1/100,000 (11). The majority of patients present with nonspecific symptoms. HEH was first identified incidentally by imaging, including ultrasonography and computed tomography (12). The etiological factors of HEH require further study; however, various risk factors have been identified, including oral contraceptives, alcohol, trauma, viral infections and chronic liver diseases (11,12). Thorotrast (thorium dioxide) (13) and vinyl chloride (14) have also been reported as risk factors.
Laboratory findings, including biochemical examination of blood, are typically non-diagnostic in cases of EHE. Tumor markers, including α-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19–9 have a potential role in excluding the diagnosis of other hepatic neoplasms (15,16). Examination of blood samples has revealed that an increase in alkaline phosphatase is the most frequently observed abnormality of HEH (12). Radiological studies, including CT, magnetic resonance imaging and angiography indicate that there are two subtypes of HEH: The nodular subtype manifests as multifocal nodules in the early stages of HEH, and these nodules grow and eventually coalesce, whereas the diffuse subtype manifests as large confluent masses preferentially involving the peripheral liver (17). In the present case, multiple nodules with capsules were observed, located peripherally in the liver, appearing with coarse calcification and peripheral enhancement when imaged using a contrast medium (Fig. 1A).
A definitive diagnosis of HEH requires histopathological examination; the predominant histological features include nests and cords of epithelioid endothelial cells and the presence of intracytoplasmic lumina. CD31, CD34 and FVIII-rAg are established endothelial cell markers that are commonly used for the diagnosis of EHE (18). As shown in Fig. 1B, the immunohistochemistry of HEH tissue samples revealed the presence of these endothelial markers.
EHE has previously been considered as an intermediate malignancy; however, the World Health Organization has now classified EHE as having full malignant potential (9,10). The metastatic rate of EHE is ~25% and mortality occurs in ~15% of all cases (1,9). By contrast, angiosarcoma of deep soft tissues metastasizes in ~50% of epithelioid angiosarcomas, and mortality occurs in over half of patients within a year of the diagnosis (19). Prognostic factors to distinguish the two biological subsets of tumors require further study to be identified.
In the present study, miRNA profiles were examined using tumor tissue samples and adjacent normal tissue samples to identify the distinguishing features of EHE and angiosarcoma. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis using Pearson's correlation demonstrated that the tumor tissues clustered separately from the normal tissues (Fig. 2). Of the 107 significantly upregulated and downregulated miRNAs identified in HEH, only miR-122-5p and miR-1290 demonstrated a differential expression pattern between HEH and angiosarcoma (Table I). miR-122-5p has previously been identified to be downregulated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, as compared with the healthy controls (20). The expression of miR-1290 has also previously been demonstrated to be associated with breast cancer prognosis (21). Interestingly, those previous reports indicate that miR-122-5p and miR-1290 were down-regulated in epithelial cancer cells. Therefore, the results of the present study suggest that EHE has similar miRNA expression patterns to epithelial cancer cells and that these expression patterns in EHE may form a different phenotype from that in angiosarcoma. In conclusion, miRNA profiling has potential as a novel biological diagnostic tool for HEH. Furthermore, miR-122-5p and miR-1290 are potential biomarkers for the accurate diagnosis of HEH in primary mesenchymal tumors of the liver.
References
- 1.Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A vascular tumor often mistaken for a carcinoma. Cancer. 1982;50:970–981. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820901)50:5<970::AID-CNCR2820500527>3.0.CO;2-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tiu CM, Chou YH, Wang HT, Chang T. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of spleen with intrasplenic metastasis: Ultrasound and computed-tomography appearance. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1992;16:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0895-6111(92)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee KC, Ng WF, Chan JK. Epithelioid haemangioendothelioma presenting as a gastric polyp. Histopathology. 1988;12:335–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ellis GL, Kratochvil FJ., III Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the head and neck: A clinicopathologic report of twelve cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986;61:61–68. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(86)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marchiano D, Fisher F, Hofstetter S. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the heart with distant metastases. A case report and literature review. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1993;34:529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kamath SM, Nagaraj HK, Mysorekar VV. Hepatic and adrenal hemangioendothelioma-a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013;7:2583–2584. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/6808.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee SE, Park HY, Kim S, Bang H, Min JH, Choi YL. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with extensive cystic change and CAMTA1 rearrangement. Pathol Int. 2013;63:502–505. doi: 10.1111/pin.12097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pokharna RK, Garg PK, Gupta SD, Dutta U, Tandon RK. Primary epithelioid haemangioendothelioma of the liver: Case report and review of the literature. J Clin Pathol. 1997;50:1029–1031. doi: 10.1136/jcp.50.12.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mentzel T, Beham A, Calonje E, Katenkamp D, Fletcher CD. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of skin and soft tissues: Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 30 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21:363–374. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199704000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moulai N, Chavanon O, Guillou L, Noirclerc M, Blin D, Brambilla E, Lantuejoul S. Atypical primary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the heart. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1:188–189. doi: 10.1016/S1556-0864(15)31539-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Neofytou K, Chrysochos A, Charalambous N, Dietis M, Petridis C, Andreou C, Petrou A. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and the danger of misdiagnosis: Report of a case. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013;2013:243939. doi: 10.1155/2013/243939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, Schemmer P, Schmied BM, Hallscheidt P, Schirmacher P, Weitz J, Friess H, Buchler MW, Schmidt J. Primary malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy. Cancer. 2006;107:2108–2121. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Soslow RA, Yin P, Steinberg CR, Yang GC. Cytopathologic features of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Diagn Cytopathol. 1997;17:50–53. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0339(199707)17:1<50::AID-DC10>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Darras T, Moisse R, Colette JM. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver. J Belge Radiol. 1988;71:722–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Okuda K, Kotoda K, Obata H, Hayashi N, Hisamitsu T. Clinical observations during a relatively early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma, with special reference to serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Gastroenterology. 1975;69:226–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haglund C, Lindgren J, Roberts PJ, Nordling S. Difference in tissue expression of tumour markers CA 19–9 and CA 50 in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1991;63:386–389. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Miller WJ, Dodd GD, III, Federle MP, Baron RL. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: Imaging findings with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159:53–57. doi: 10.2214/ajr.159.1.1302463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Makhlouf HR, Ishak KG, Goodman ZD. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: A clinicopathologic study of 137 cases. Cancer. 1999;85:562–582. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990201)85:3<562::AID-CNCR7>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG. Angiosarcoma of soft tissue: A study of 80 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:683–697. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199806000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tan Y, Ge G, Pan T, Wen D, Gan J. A pilot study of serum microRNAs panel as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014;9:e105192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Endo Y, Yamashita H, Takahashi S, Sato S, Yoshimoto N, Asano T, Hato Y, Dong Y, Fujii Y, Toyama T. Immunohistochemical determination of the miR-1290 target arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:990. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


