Figure 1.
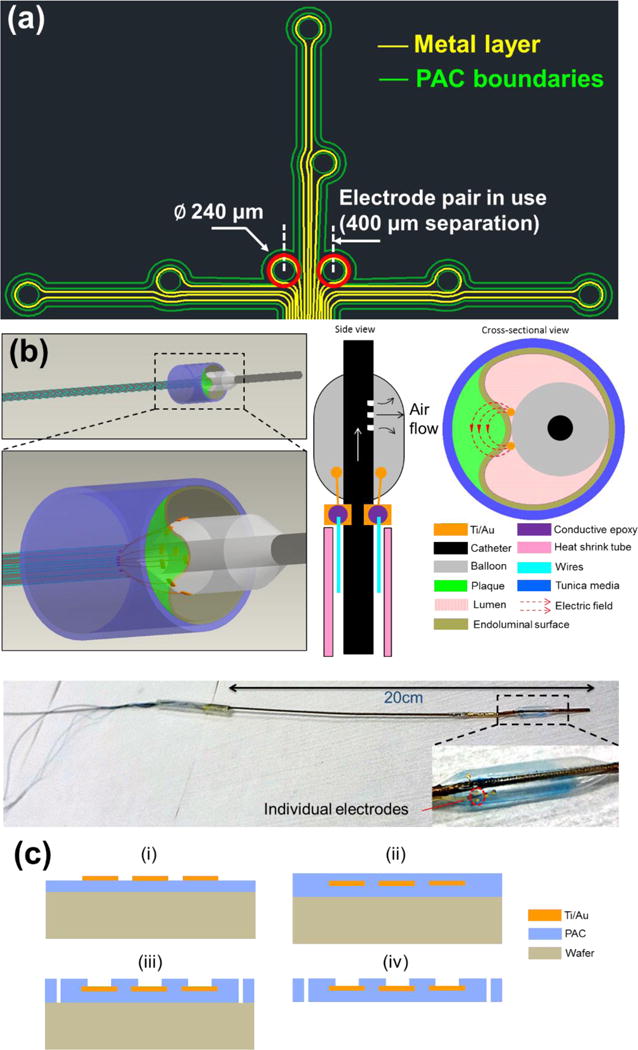
(a) Design schematic of an array of individually addressable impedance sensing electrodes. A set of eight round electrodes (Ø 240 μm) was implemented. The electrode pair situated in the center (400 μm separation) and highlighted in red was selected for measurements throughout the study. (b) 3D rendering of the deployed EIS sensor in contact with a plaque, and 2D side-view of the device illustrating microelectrode placement with adjacent 2D cross-sectional view illustrating apposition and contact of the electrodes on the inflated balloon with the endoluminal surface covering an atherosclerotic plaque. Generated electric fields between the 2 microelectrodes are illustrated. An image of the actual EIS sensor with close-up view of flexible electrodes attached on the inflated balloon is provided. (c) Schematics of the microfabrication process of the flexible PAC electrodes (i–iv).
