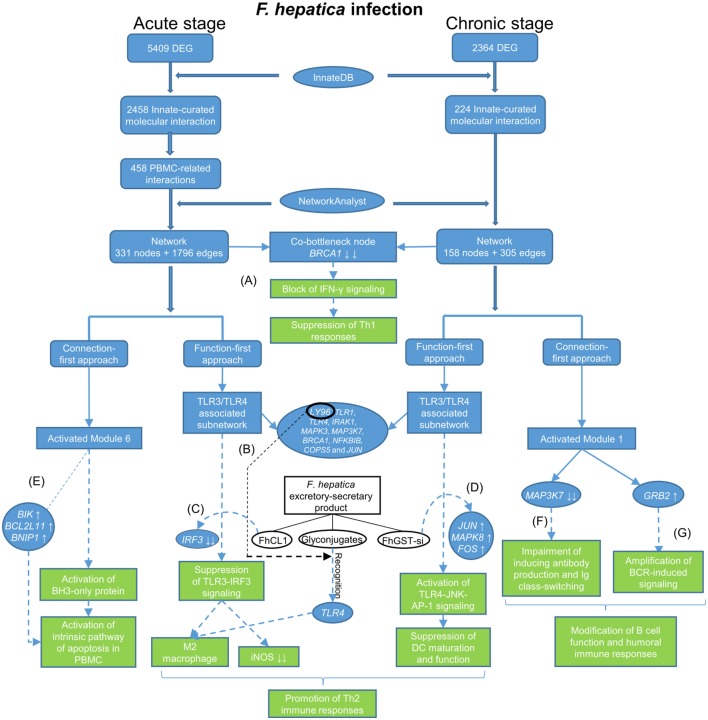
Figure 5.
Flow diagram showing data process and how the main findings lead to a better understanding of immune responses to Fasciola hepatica infection. The blue tabs and solid arrows refer to the pipeline of data mining and main results. The green tabs and dotted arrows refer to hypothesis generation: (A) F. hepatica infection may block IFN-γ signaling through consistently suppressing the transcript expression of breast cancer 1. (B) LY96 may play a role in recognition of fluke-derived glycan residues by Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in macrophages. (C) F. hepatica cathepsin L1 (FhCL1) induces M2 macrophage phenotypes through blocking TLR3-IRF3 pathway, possibly by decreasing transcript expression of IRF3. (D) F. hepatica sigma class glutathione transferase (FhGST-si) suppresses dendritic cells maturation through activating TLR4-JNK-AP-1 pathway, possibly by increasing transcript expression of JUN, MAPK8, and FOS. (E) F. hepatica may induce apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells through intrinsic pathway, possibly by increasing transcript expression of BIK, BCL2L11, and BNIP1. (F) F. hepatica infection may modulate humoral immune responses through regulating transcript expression of MAP3K7. (G) F. hepatica infection may modulate B-cell receptor signaling through activating growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 transcript expression.