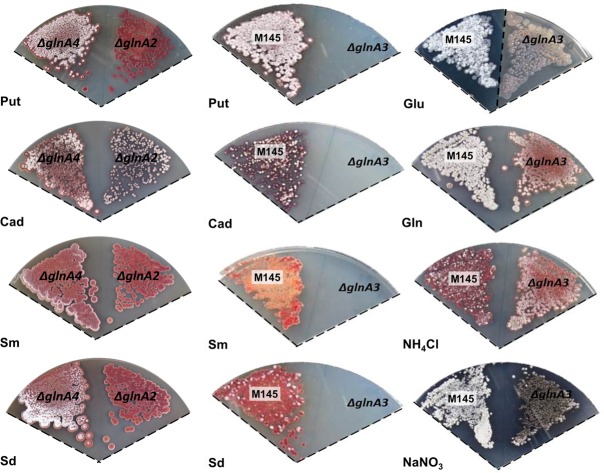
FIGURE 3.
Physiological role of the glnA3 gene product in S. coelicolor M145 cells grown in the presence of polyamines. (A) Phenotypic comparison of parental strain S. coelicolor M145 and ΔglnA2, ΔglnA3, and ΔglnA4 mutants grown on defined Evans medium supplemented with Put – putrescine dihydrochloride (200 mM), Cad – cadaverine dihydrochloride (50 mM), Sm – spermine tetrahydrochloride (25 mM), Sd – spermidine trihydrochloride (25 mM) as well as on Glu – monosodium glutamate (50 mM), Gln – glutamine (50 mM), NH4Cl – ammonium chloride (50 mM) and NaNO3 – sodium nitrate (50 mM) as sole nitrogen source. Each panel represents observations on a single agar plate, except the phenotypic analysis of the glnA3 mutant and parental strain in the presence of glutamate has been documented on two separate agar plates as indicated by the dotted line. Deletion of glnA3 resulted in the no-growth phenotype in the presence of high polyamine concentrations.