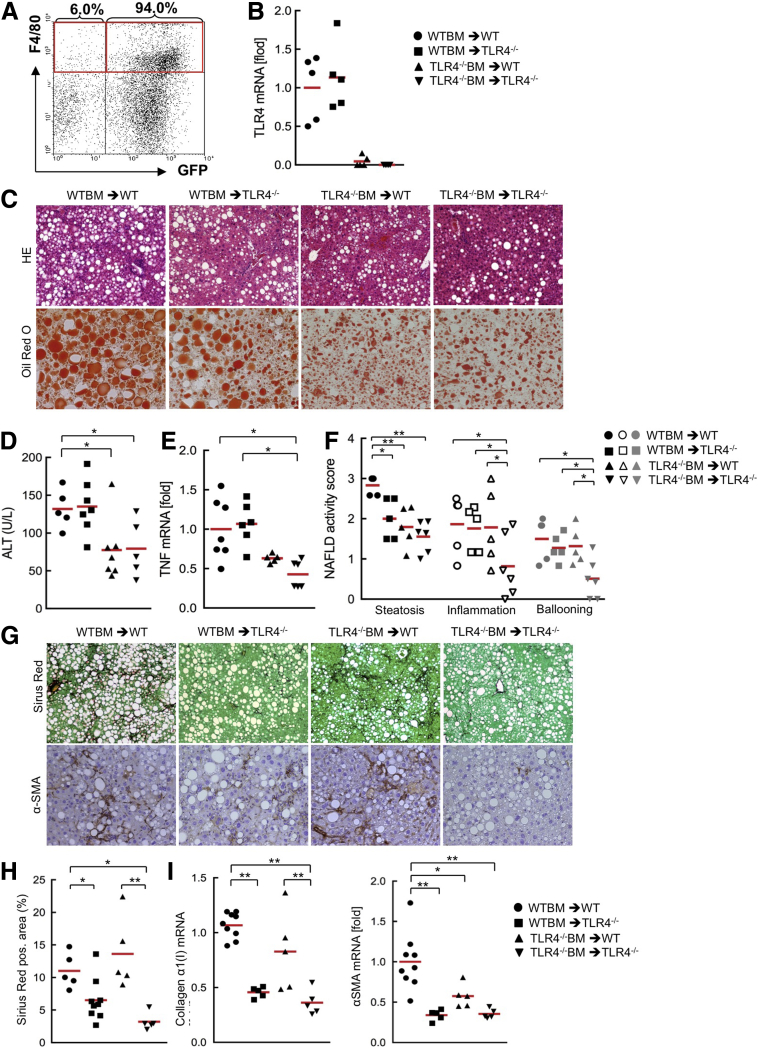
Figure 1.
BM-derived and resident liver cells are required for TLR4-mediated hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in the murine NASH model induced by CDAA diet. (A) Wild-type mice were transplanted with BM from β-actin promoter-driven GFP-transgenic mice after whole-body irradiation. After 2 weeks of BMT, liposomal clodronate was injected. After 10 weeks of BMT, liver nonparenchymal cell fraction was separated and F4/80-positive GFP-expressing cells were examined by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis. (B–I) The TLR4 BM chimeric mice were fed the CDAA diet for 22 weeks (n = 5-9, each). (B) The successful engraftment of donor BM cells into TLR4 BM chimeric mice was determined by TLR4 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in spleen cells. (C) Hepatic inflammation and steatosis were evaluated by H&E staining and Oil Red O staining, respectively. Original magnification, ×100 for H&E, and ×200 for Oil Red O. (D) ALT levels. (E) Hepatic TNF mRNA levels were measured by quantitative PCR. (F) NAFLD activity score. (G) Liver sections were stained with Sirius Red and used for immunohistochemistry for α-SMA. Original magnification, ×100 for Sirius Red staining, and ×200 for α-SMA staining. (H) Quantifications of Sirius red staining. (I) Hepatic fibrogenic genes (collagen α1[I], α-SMA) were determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Similar results were obtained in 2 independent experiments. A representative result is shown. *P < .05, **P < .01. WT, wild type. Red horizontal bars represent average.