Fig. (1).
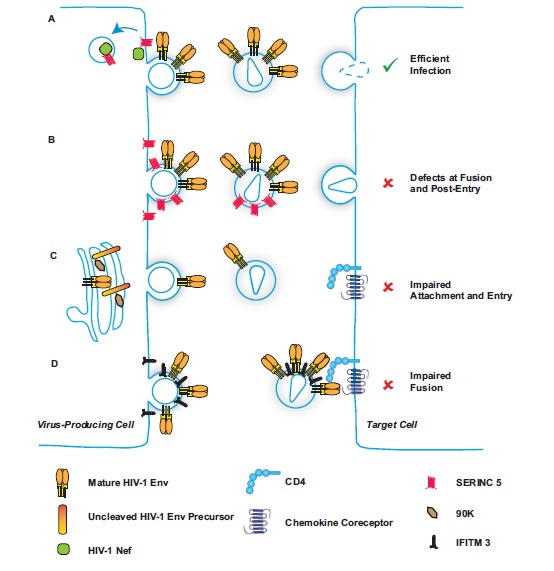
Particle infectivity is modulated by viral and cellular factors. (A) In the course of wild-type HIV-1 infection, HIV-1 Nef downregulates antiviral SERINC5 from the cell surface in a clathrin-dependent manner, thus preventing incorporation of this small transmembrane protein into nascent virions. (B) In the absence of HIV-1 Nef expression, SERINC5 incorporates into budding particles, inducing defects at fusion and post-entry following infection of the target cell. (C) Cellular 90K expression in the virus-producing cell induces a defect in posttranslational maturation of HIV-1 Env and prevents efficient viral incorporation of cleaved HIV-1 Env, resulting in poor ability of particles to attach and enter new target cells. (D) IFITM3 incorporates into HIV-1 virions and prevents fusion with the target cells during cell-to-cell transmission.
