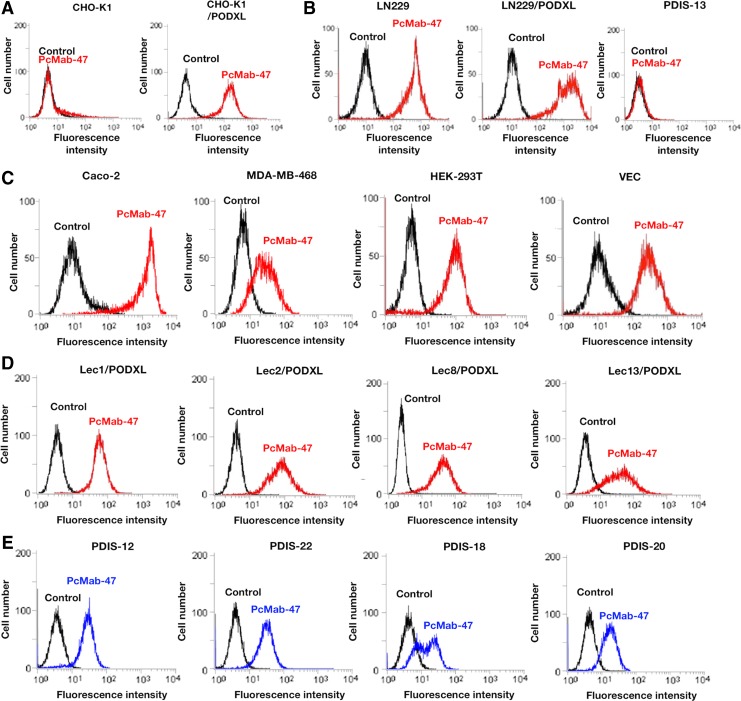
FIG. 1.
Specific detection of PODXL by PcMab-47 using flow cytometry. (A) CHO-K1 and CHO-K1/PODXL were treated with PcMab-47 (1 μg/mL; red) or control PBS (black) for 30 minutes at 4°C, followed by treatment with antimouse IgG-Oregon green. (B) LN229, LN229/PODXL, and PDIS-13 (LN229/PODXL-knockout cells) were treated with PcMab-47 (1 μg/mL; red) or control PBS (black) for 30 minutes at 4°C, followed by treatment with antimouse IgG-Oregon green. (C) Caco-2, MDA-MB-468, HEK-293T, and vascular endothelial cells were treated with PcMab-47 (1 μg/mL; red) or control PBS (black) for 30 minutes at 4°C, followed by treatment with antimouse IgG-Oregon green. (D) Lec1 (N-glycan-deficient CHO)/PODXL, Lec2 (sialic acid-deficient CHO)/PODXL, Lec8 (galactose-deficient CHO)/PODXL, and Lec13 (fucose-deficient CHO)/PODXL were treated with PcMab-47 (1 μg/mL; red) or control PBS (black) for 30 minutes at 4°C, followed by treatment with antimouse IgG-Oregon green. (E) PDIS-12 (N-glycan-deficient HEK-293T), PDIS-22 (sialic acid-deficient HEK-293T), PDIS-18 (galactose-deficient HEK-293T), and PDIS-20 (N-glycan/sialic acid/galactose-deficient HEK-293T) were treated with PcMab-47 (1 μg/mL; blue) or control PBS (black) for 30 minutes at 4°C, followed by treatment with antimouse IgG-Oregon green. Fluorescence data were collected using the Cell Analyzer EC800. PBS, phosphate buffered saline; PODXL, podocalyxin.