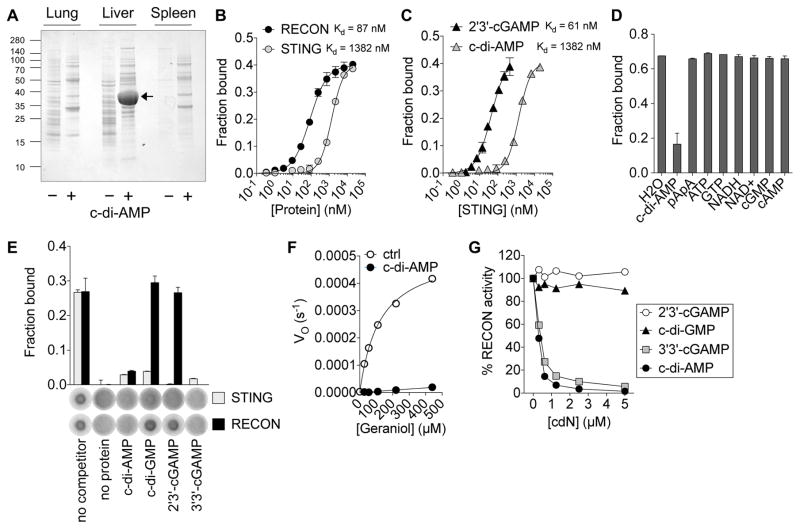
Figure 1. Bacterial cyclic dinucleotides bind and inhibit the oxidoreductase RECON.
(A) SDS-page analysis of pull-downs from mouse organ lysates with c-di-AMP (+) or control (−) sepharose.
(B) Binding titration of 32P-c-di-AMP with RECON or STING. Kd values are indicated.
(C) Binding titration of 32P-2′3′-cGAMP or 32P-c-di-AMP with STING.
(D) Binding of RECON with 32P-c-di-AMP in the presence of competing unlabeled nucleotides (200 μM).
(E) Binding of RECON or STING with 32P-c-di-AMP in the presence of competing unlabeled cyclic dinucleotides, each at 400 μM concentration.
(F) Michaelis–Menten kinetics of RECON with the substrate geraniol and cosubstrate NAD+ in the presence or absence of 1 μM c-di-AMP.
(G) RECON enzyme activity in the presence of increasing concentrations of the indicated cdNs. Substrate was 9,10-PQ and cosubstrate was NADPH.
Data are plotted as percent of activity without any cdN added. Data are representative of two (A, C, D, E, G) or three (B, F) independent experiments with similar results. In all panels, error bars represent ± SEM of technical replicates. See also Figure S1.