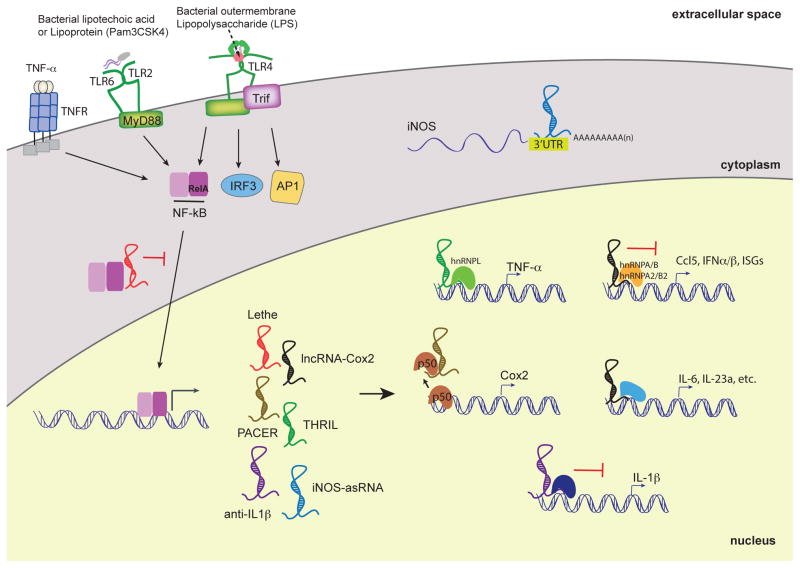
Figure 2.
LncRNAs functions in TLR-dependent inflammatory responses in myeloid cells. lncRNAs are induced by PRRs such as TLRs and TNFR. Upon PRR activation, the transcription factor NF-κB translocates to the nucleus and induces the expression of various lncRNAs. Their proposed functions are either nuclear, where they can activate or repress the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Lethe binds to RelA, a subunit of NF-kB, to sequester and prevent binding to NF-kB-target promoters. PACER binds to the p50 subunit of NF-kB and modulates the basal levels of Cox2. Anti-IL1β inhibits IL-1β transcription via chromatin remodeling. LincRNA-Cox2 possesses suppressive functions by interacting with hnRNP-A/B and A2/B1 and activating functions through yet-to-be discovered mechanisms. THRIL regulates TNFα expression through its interaction with hnRNP-L. iNOS-asRNA, mediates its cis-activity is in the cytoplasm and stabilizes the iNOS mRNA transcript. In order to more thoroughly understand lncRNA-dependent innate immunoregulatory functions, the interferon pathway mediated by IRFs and the MAP kinase pathway will need to be more deeply explored.