FIG 7.
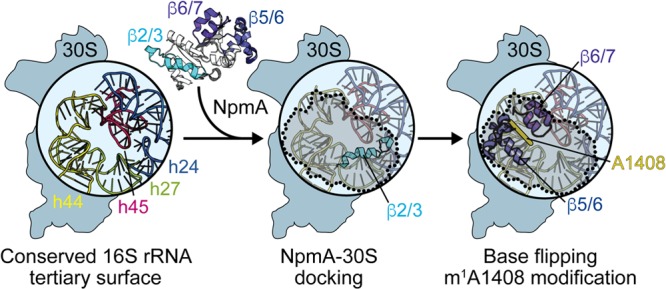
Model for NpmA action. (Left) The structurally conserved 16S rRNA tertiary surface, comprising helices 24, 27, 44, and 45, that is bound by aminoglycoside resistance methyltransferase enzymes. NpmA docking on the 30S subunit is driven by interactions made by the β2/3 linker (center), while conformational changes and specific residues within the β5/6 and β6/7 linkers control base flipping and methyltransferase activity (right). 30S-bound NpmA is denoted by the shaded area outlined with dotted lines.
