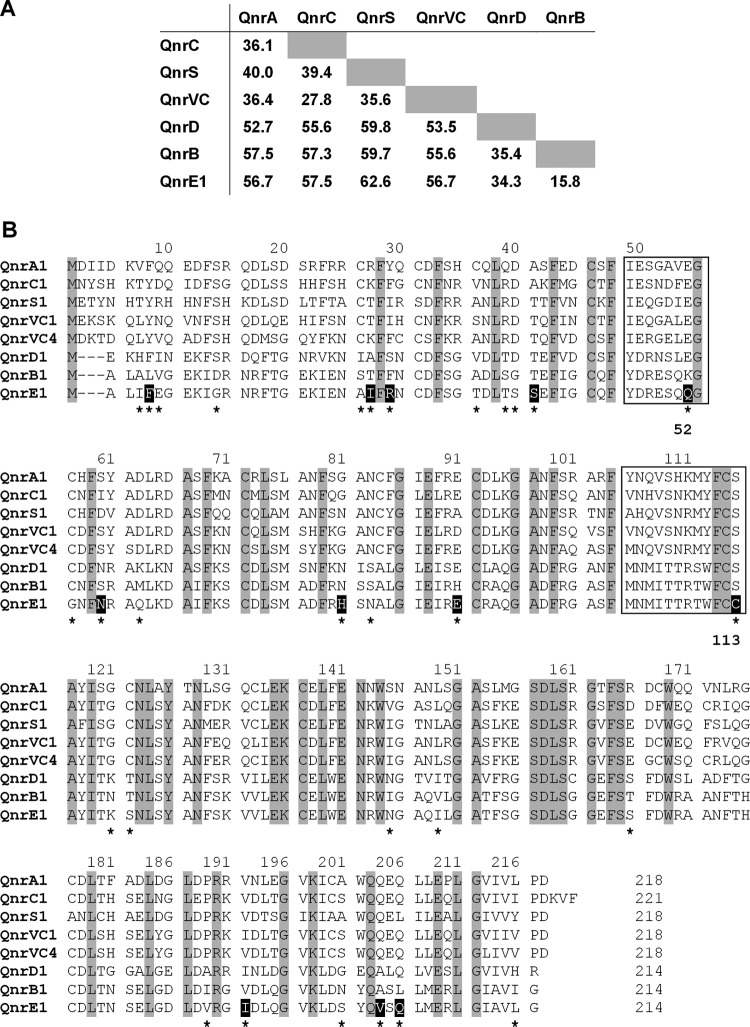
FIG 1.
Comparison of Qnr proteins. (A) Paired comparisons of Qnr families. The averages of the percentage of amino acid differences between the indicated families are shown. (B) Pentapeptide repeat structures of Qnr proteins. Only representative variants for the six families are shown. Gaps introduced to maximize the alignment are indicated by hyphens. The amino acid numbering indicated above each block of sequences is based on the longest protein (QnrC1). Residues fully conserved among all of the Qnr variants shown are depicted with a gray-shaded background. The loops A and B (8 and 12 amino acids, respectively), essential for the quinolone-protective activity of the Qnr proteins, are indicated by boxes. The amino acid changes between QnrE1 and QnrB1 are marked with asterisks, and those located in positions for which no changes were found between QnrB1 and any of the remaining QnrB proteins previously described are highlighted with a black-shaded background. The locations in the loops A and B of the changes between QnrE1 and QnrB1 are indicated by bold numbers (QnrB amino acid numbering) below the block of sequences.