Fig. 2.
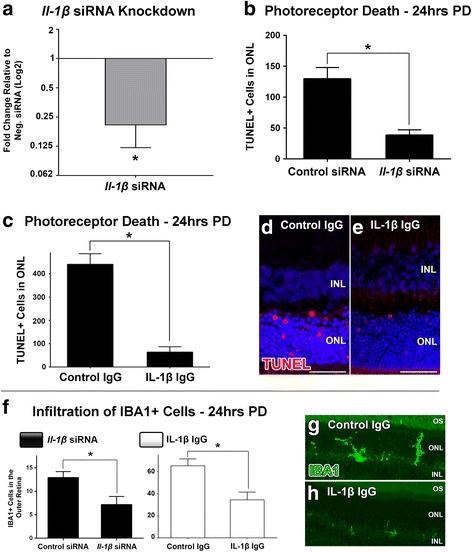
Effect of IL-1β inhibition on photoreceptor apoptosis and macrophage infiltration following photo-oxidative damage (PD). a A significant knockdown of Il-1β expression in the retina was achieved in retinas injected with an Il-1β-specific siRNA, compared to the negative control siRNA group (P < 0.05). b The number of TUNEL+ cells in the ONL was reduced in Il-1β siRNA-injected retinas after photo-oxidative damage, compared to controls (P < 0.05) c A reduction in the number of TUNEL+ cells in the ONL was also documented in animals that had been intravitreally injected with an IL-1β neutralising antibody prior to photo-oxidative damage, in comparison to an isotype control antibody (P < 0.05). d-e Representative images showcase a decrease in TUNEL+ profiles (red) in retinal section from the IL-1β neutralisation group (e), compared to a section from the isotype control group (d). f The infiltration of IBA1-immunolabelled macrophages into the outer retina (ONL and subretinal space) following photo-oxidative damage was significantly decreased in animals injected with either Il-1β-specific siRNA or an IL-1β-specific neutralising antibody, compared to their respective controls (P < 0.05). g-h Representative images of IBA1-immunolabelled macrophages demonstrate the reduction in IBA1+ cells in the outer retina in the IL-1β antibody neutralisation retinas compared to controls (green). INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. N = 4-5 per group. Asterisks denote a significant change, where P < 0.05. Scale bars equate to 25 μm
