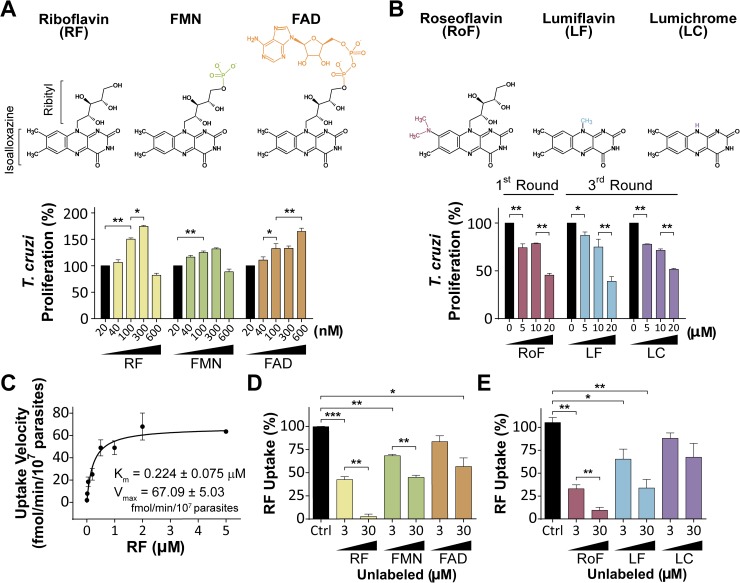
Fig 1. Flavins and chemical analogs are incorporated into T. cruzi epimastigotes and affect their proliferation with opposite effects.
Chemical structures of riboflavin, FMN and FAD, and their analogs roseoflavin, lumiflavin and lumichrome are shown in A and B top panels. A and B bottom panels: T. cruzi Y strain epimastigotes were maintained at 28°C until stationary phase, then washed and incubated in fresh medium with the indicated compound concentrations: (A) flavins and (B) chemical analogs plus 300 nM riboflavin. Parasites were counted daily. T. cruzi proliferation (%) was calculated at the indicated round using fifth day-counts and control conditions -(A) 20 nM flavins or (B) 0 μM analogs- as references (100%). Log-phase Y strain epimastigotes grown in BHT-10% FBS were harvested, washed, resuspended in PBS-2% glucose and incubated at 37°C. (C) Riboflavin uptake velocity was calculated at 0–5 μM final substrate concentration. Aliquots were sampled at 0 and 5 min after the addition of radioactive material. Displacement assays were performed at 0.3 μM radioactive riboflavin mix (Ctrl: control, 100%) and 3–30 μM of (D) unlabeled flavins (RF, FMN or FAD) or (E) unlabeled analogs (RoF: roseoflavin, n = 3; LF: lumiflavin, n = 4; or LC: lumichrome; n = 4). Values are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by one way ANOVA test followed by a post-hoc Tukey's multiple comparison test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005).