EXTENDED DATA FIGURE 5. A1 astrocytes are morphologically simple.
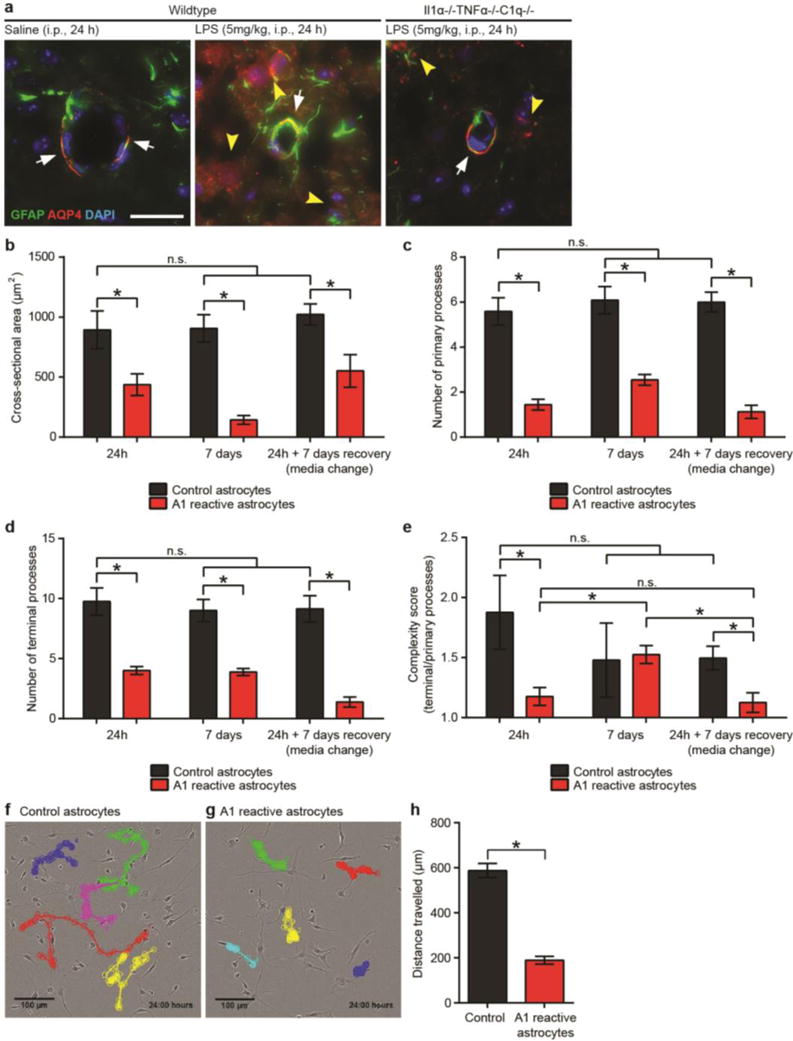
a, in vivo immunoflourescent staining for the water channel AQP4 and GFAP. Saline injected (control) mice had robust AQP4 protein localization to astrocytic endfeet on blood vessels (red stain, white arrows), while LPS injected mice had loss of polarization of AQP4 immunoreactivity, with bleeding of immunoreactivity away from endfeet (white arrows) and increased staining in other regions of the astrocyte (yellow arrowheads). Triple knock-out mice (Il1α−/−TNFα−/−C1q−/−) did retained AQP4 immunoreactivity in endfeet following LPS-induced neuroinflammation (white arrows), though some low-level ectopic immunoreactivty was still seen (yellow arrowheads). b–e, Quantification of cell morphology of GFAP-stained cultured astrocytes in resting or A1 reactive state: cross-sectional area (b), number of primary processes extending from cell soma (c), number of terminal branchlets (d), ratio of terminal to primary processes (complexity score, e). f, g, time-lapse tracing of control (f) and A1 reactive (g) astrocytes. Quantification shown in panel (h). A1 reactive astrocytes migrated approximately 75% less than control astrocytes over a 24 h period. * p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
