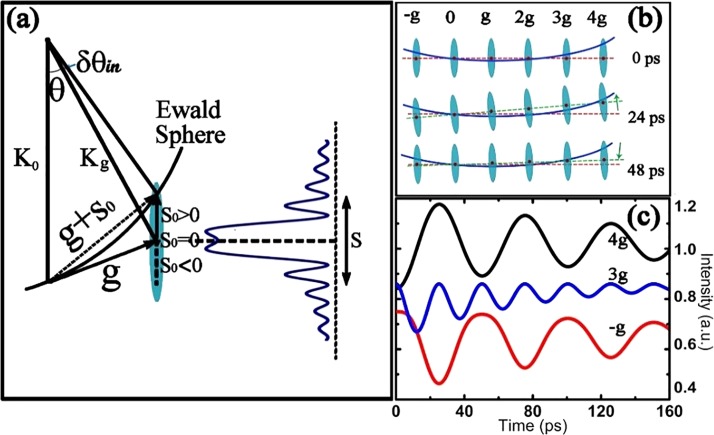
FIG. 5.
(a) Sketch of the crystal dynamic diffraction theory; the Bragg peak intensity as a function of deviation parameter s is shown as a blue curve. (b) Temporal evolution of the intersections of the Ewald sphere (blue curvature line) with the reciprocal rods, which is modulated by the breath oscillation of the thin crystal along the c axis; the red line is the horizontal reference line, and the green line represents the reciprocal plane. The oscillation period is set to be 48 ps, and typical positions for three time delays are displayed. (c) Three simulated results for H = −g, 3g, and 4g, clearly illustrating the appearance of two out-of-phase oscillations (4g, −g) and a half-period oscillation (3g) arising from coupling between the excitation coherent lattice oscillation and the dynamic diffraction effect.