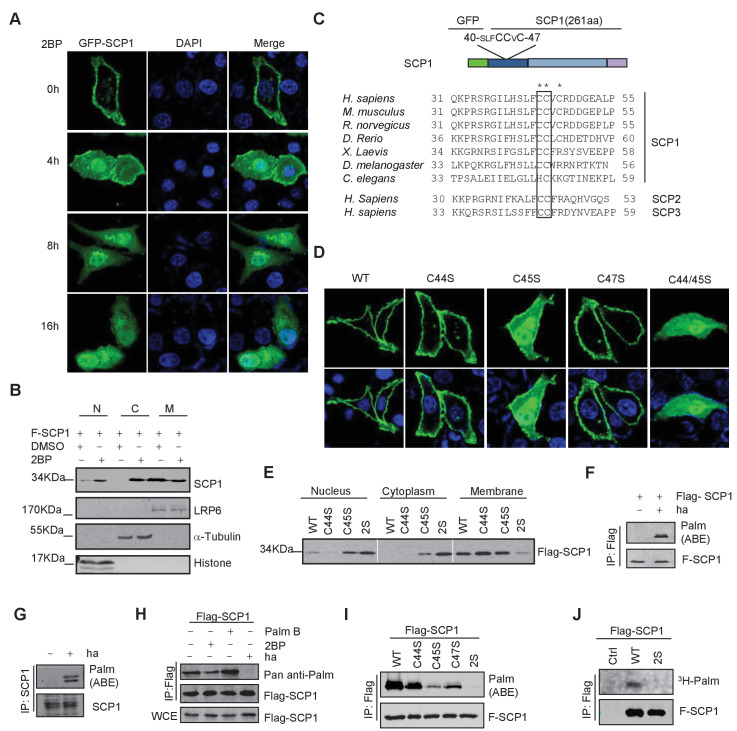
Figure 2. SCP1 was palmitoylated.
(A) Palmitoylation inhibitor 2-bromopalmitate (2BP) blocked the SCP1 membrane localization. HeLa cells were transfected and treated with 2BP (10 μM) for 4, 8, or 16 h or DMSO as a control. The subcellular localization of SCP1 was detected using immunofluorescence assay. (B) HEK293T cells were treated with DMSO or 2BP (10 μM) for 6 h and the subcellular location of SCP1 was detected using western blotting. (C) Potential palmitolylation sites Cys44 and Cys45 of SCP1 were evolutionarily conserved. Amino acids 33–55 of SCP1 in different species, ranging from Caenorhabditis elegans to Homo sapiens, 30–53 of SCP2 in H. sapiens, and 33–59 of SCP3 in H. sapiens are shown. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with WT-SCP1, C44S-SCP1, C45S-SCP1, C47S-SCP1, and C44/45S(2S)-SCP1 for 24 h. The subcellular localizations of WT-SCP1 and its mutants were detected using immunofluorescence assay. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with WT-SCP1, C44S-SCP1, C45S-SCP1, and C44/45S(2S)-SCP1 for 24 h and cell fractions of were analyzed using western blotting. (F) FLAG-SCP1 was expressed in HEK293T cells, immunoprecipitated, and palmitoylation was detected using the acyl–biotin exchange (ABE) assay. (G) Palmitoylation of endogenous SCP1 in HEK293T cells was detected using the ABE assay. (H) FLAG-SCP1 was expressed in HEK293T cells for 24 h and treated with 2BP (10 μM) or palmostatin B (50 μM) for 12 h. Palmitoylation of SCP1 was detected using pan-palmitoylation antibody. (I) and (J) Identification of palmitoylation sites using the ABE assay (I) and the [3H] palmitate incorporation assay (J).