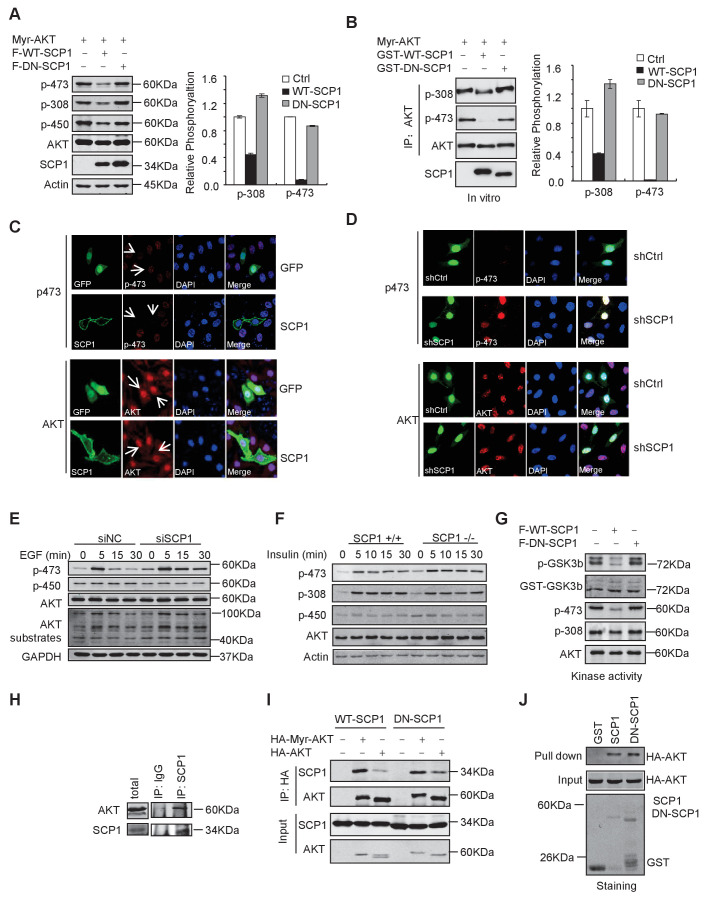
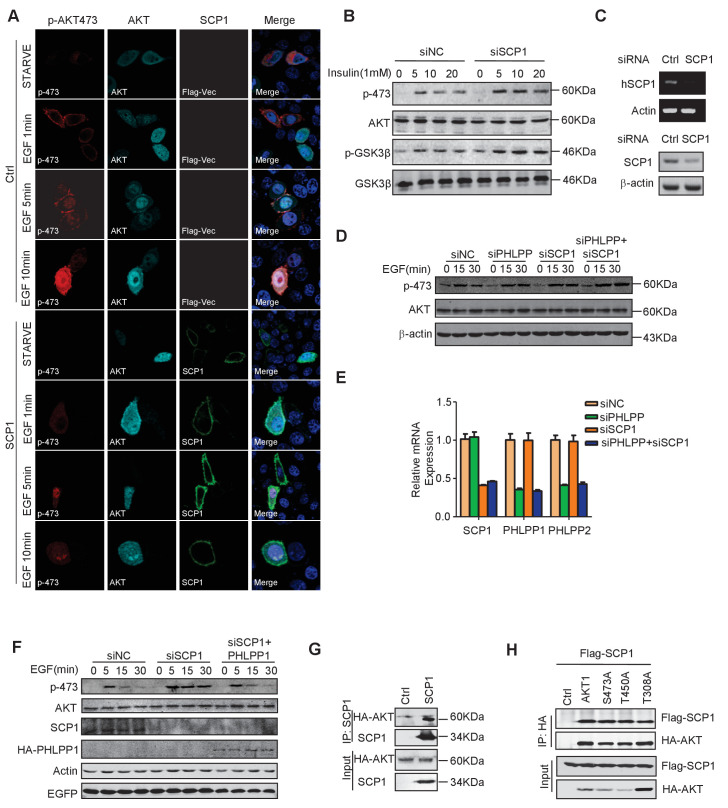
Figure 5. SCP1 dephosphorylated AKT.
(A) Wild-type (WT)-SCP1 dephosphorylated AKT Ser473. Myr-AKT was co-expressed with vector, WT-SCP1, or DN-SCP1. The phosphorylations of p-Ser473-AKT, p-Thr308-AKT, and p-Thr450-AKT was analyzed using western blotting. The relative phosphorylations of p-Thr308-AKT and p-Thr450-AKT are displayed in the form of a histogram. (B) WT-SCP1 dephosphorylated AKT in vitro. HA-Myr-AKT was immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells and incubated with purified GST, GST-WT-SCP1, or GST-DN-SCP1 for 30 min. The phosphorylations of p-Ser473-AKT and p-Thr308-AKT were analyzed using western blotting. (C) WT-SCP1 dephosphorylated AKT in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-SCP1 for 24 h. The phosphorylation of p-Ser473-AKT and total AKT was detected using immunofluorescence assay. (D) SCP1 knockdown promoted AKT Ser473 phosphorylation in HeLa cells. Control or Ctdsp1 shRNA was transfected into HeLa cells for 72 h. The phosphorylation of p-Ser473-AKT and total AKT was detected using immunofluorescence assay. (E) SCP1 knockdown promoted EGF-induced AKT activity. H1299 cells were transfected with control or Ctdsp1 siRNA for 72 h. The cells were stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml) as indicated after 8 h of starvation, and phosphorylation of AKT was detected using immunofluorescence assay. (F) SCP1 depletion promoted insulin-stimulated AKT activation. Ctdsp1+/+ or Ctdsp1–/–MEFs (mouse embryonic fibroblast) were stimulated with insulin (1 mM) as indicated after 6 h of starvation. (G) WT-SCP1 decreased the AKT kinase activity. AKT was transfected into HEK293T cells with vector, WT-SCP1, or DN-SCP1, immunoprecipitated, and incubated with GST-GSK3β. The phosphorylation of GSK3β was measured using western blotting. (H) Endogenous AKT interacted with endogenous SCP1. Endogenous SCP1 was immunoprecipitated using an anti-SCP1 antibody and the associated AKT was detected using an anti-AKT antibody. (I) The interaction of SCP1 with WT or myristoylated AKT1 is independent of its phosphatase activity. (J) Purified GST, GST-WT-SCP1, and GST-DN-SCP1 were incubated with cell lysates overexpressing AKT. The interaction was detected using western blotting.